Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generally higher than that of the corresponding halo acids. Explain.
उत्तर १
Both acidic (carboxyl) as well as basic (amino) groups are present in the same molecule of amino acids. In aqueous solutions, the carboxyl group can lose a proton and the amino group can accept a proton, thus giving rise to a dipolar ion known as a zwitter ion.
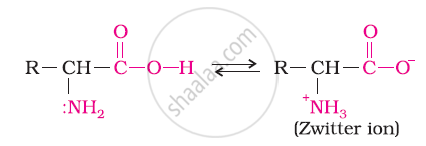
Due to this dipolar behaviour, they have strong electrostatic interactions within them and with water. But halo-acids do not exhibit such dipolar behaviour.
For this reason, the melting points and the solubility of amino acids in water is higher than those of the corresponding halo-acids.
उत्तर २
The amino acids exist as zwitter ions, H3N+ — CHR-COO-. Due to this dipolar salt like character, they have strong dipole-dipole attractions. Therefore, their melting points are higher than corresponding haloacids which do not have salt like character.
Due to salt like character, amino acids intereact strongly with water. As a result, their solubility in water is higher than corresponding haloacids which do not have salt like character.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why?
Define the following terms: Essential amino acids
Write the correct reaction for formation of the peptide bond between amino acids
What is the difference between acidic amino acids and basic amino acids?
Differentiable between the following:
Essential amino acids Non-essential amino acids
The number of tripeptides formed by 3 different amino acids.
Which amino acids are chiral?
Among the following a chiral amino acid is:
Match the following:
| I | II |
| (i) Amino acids | (A) protein |
| (ii) Thymine | (B) Nucleic acid |
| (iii) Insulin | (C) DNA |
| (iv) phosphodiester linkage | (D) Zwitter ion |
Which of the following is the best matched options?
Which of the following acids is a vitamin?
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Amino acids can be classified as α–, β–, γ–, δ– and so on depending upon the relative position of amino group with respect to carboxyl group. Which type of amino acids form polypetide chain in proteins?
Describe the term D- and L- configuration used for amino acids with examples.
X – Amino acid behave as crystalline ionic solid and have high melting-point due to the present of:-
Which of the following is a basic amino acid?
Why tryptophan is an essential amino acid?
Define Zwitter ion
