Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The molecules having triple bond in them are:
(a) oxygen and ethyne
(b) carbon dioxide and ammonia
(c) methane and ethene
(d) nitrogen and ethyne
उत्तर
(d) nitrogen and ethyne
In a nitrogen molecule, each nitrogen atom shares its 3 electrons to form a triple bond among them. In an ethyne molecule, each carbon atom shares 3 electrons to form a triple bond among them.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds?
How does graphite act as a lubricant?
Give one example of a molecule containing a double covalent bond
Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding?
Why is diamond used for making cutting tools (like glass cutters) but graphite is not?
What type of bonding would you expect between Hydrogen and Chlorine?
A saturated hydrocarbon has fifty hydrogen atom in its molecule. The number of carbon atoms in its molecule will be
(a) twenty five
(b) twenty four
(c) twenty six
(d) twenty seven
An element E exists in three allotropic forms A, B and C. In allotrope A, the atoms of element E are joined to form spherical molecules. In allotrope B, each atom of element E is surrounded by three other E atoms to form a sheet like structure. In allotrope C, each atom of element E is surrounded by four other E atoms to form a rigid structure.
(a) Name the element E.
(b) What is allotrope A.
(c) What is allotrope B?
(d) What is allotrope C?
(e) Which allotrope is used in making jewellery?
(f) Which allotrope is used in making anode of a dry cell?
What happens when methane (natural gas) burns in air? Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Define a coordinate bond and give the conditions for its formation.
Give examples for the following:
Two gaseous polar compounds.
Give examples for the following:
Two gaseous non polar compounds.
What do you understand by dipole (polar) molecule?
State the type of bond formed when the combining atom has small E.N. difference.
Give an example of the covalent bond formed by
(i) Similar atoms (ii) Dissimilar atoms
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
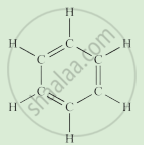 |
The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is -
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H}\ce{H-C-H}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{C - H}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\]
Explain dipole (polar) molecule by taking hydrogen chloride as an example.
