Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permittivity (εr) and relative permeability (µr). The refractive index is defined as `sqrt(µ_r ε_r) = n`. For ordinary material εr > 0 and µr > 0 and the positive sign is taken for the square root. In 1964, a Russian scientist V. Veselago postulated the existence of material with εr < 0 and µr < 0. Since then such ‘metamaterials’ have been produced in the laboratories and their optical properties studied. For such materials `n = - sqrt(µ_r ε_r)`. As light enters a medium of such refractive index the phases travel away from the direction of propagation.
- According to the description above show that if rays of light enter such a medium from air (refractive index = 1) at an angle θ in 2nd quadrant, them the refracted beam is in the 3rd quadrant.
- Prove that Snell’s law holds for such a medium.
उत्तर
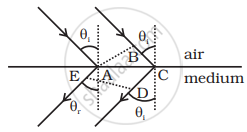
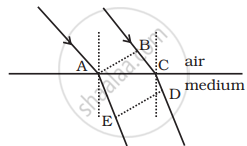
i. If given postulate is true, then two parallel rays would proceed as shown in figure (i).
Metamaterials with positive refractive index
Ordinary material with positive refractive index
Again consider figure (i), let AB represent the incident wavefront and DE represent the refracted wavefront. All points on a wavefront must be in the same phase and in turn, must have the same optical path length.
Thus `- sqrt(ε_rµ_r) AE = BC - sqrt(ε_rµ_r) CD`
or `BC = sqrt(ε_rµ_r) (CD - AE)`
`BC > 0, CD > AE`
As showing that the postulate is reasonable. If however, the light proceeded in the sense it does for ordinary material (viz in the fourth quadrant, figure)
Then, `- sqrt(ε_rµ_r) AE = BC - sqrt(ε_rµ_r) CD`
or `BC = sqrt(ε_rµ_r) (CD - AE)`
If `BC > 0` then `CD > AE`
This is obvious from figure (i). Hence, the postulate is resonable.
However, if the light proceeds in the sense it does for ordinary material (going from 2nd quadrant to 4th quadrant) as shown in figure (i) then proceeding as above
`- sqrt(ε_rµ_r) AE = BC - sqrt(ε_rµ_r) CD`
or `BC = sqrt(ε_rµ_r) (CD - AE)`
As AE > CD, therefore BC < 0 which is not possible. Hence, the given postulate is correct.
ii. From figure (i),
`BC = AC sin theta_i`
And `CD - AE = AC sin theta_r`
As `BC = - sqrt(ε_rµ_r) AC sin theta_r`
∴ `AC sin theta_i = sqrt(ε_rµ_r) AC sin theta_r`
or `sin theta_i/sin theta_r = sqrt(ε_rµ_r) = n`
Which proves Snell's law.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The refractive index of glass is 1.5. What is the speed of light in glass? (Speed of light in vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m s−1)
Explain how Corpuscular theory predicts the speed of light in a medium, say, water, to be greater than the speed of light in vacuum. Is the prediction confirmed by experimental determination of the speed of light in water? If not, which alternative picture of light is consistent with the experiment?
Let us list some of the factors, which could possibly influence the speed of wave propagation:
(i) Nature of the source
(ii) Direction of propagation
(iii) Motion of the source and/or observer
(iv) Wavelength
(v) Intensity of the wave
On which of these factors, if any, does the speed of light in vacuum?
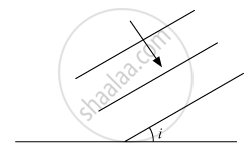
A plane wavefront propagating in a medium of refractive index 'μ1' is incident on a plane surface making the angle of incidence 'i' as shown in the figure. It enters into a medium of refractive index 'μ2' (μ2 > μ1). Use Huygens' construction of secondary wavelets to trace the propagation of the refracted wavefront. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
The wavefronts of light coming from a distant source of unknown shape are nearly _________ .
Light waves travel from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium. Its velocity decreases bec;ause of change in ______.
In the figure, the optical fibre is l = 2 m long and has a diameter of d = 20 µm. If a ray of light is incident on one end of the fiber at angle θ1 = 40°, the number of reflections it makes before emerging from the other end is close to ______.
(Refractive index of fiber is 1.31 and sin40° = 0.64)

A glass slab of thickness 4 cm contains the same number of waves as 5 cm of water. When both are traversed by the same monochromatic light. If the refractive index of water is `(4/3)`. What is that of glass?
A light ray in a medium (RI = 5/3) enters another medium at an angle of 30°. The angle in the other medium is sin-1 (5/6). The incident angle must be increased such that the ray is completely reflected at minimum degrees is ______.
Using Huygens’s construction of secondary wavelets draw a diagram showing the passage of a plane wavefront from a denser to a rarer medium. Using it verifies Snell’s law.
