Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The radius of the shortest orbit in a one-electron system is 18 pm. It may be
पर्याय
hydrogen
deuterium
He+
Li++
उत्तर
Li++
The radius of the nth orbit in one electron system is given by
`r_n = (n^2a_0)/Z`
Here, a0 = 53 pm
For the shortest orbit,
n = 1
For hydrogen,
Z = 1
∴ Radius of the first state of hydrogen atom = 53 pm
For deuterium,
Z= 1
∴ Radius of the first state of deuterium atom = 53 pm
For He+,
Z = 2
∴ Radius of He+ atom =`53/2 pm = 26.5 "pm"`
For Li++,
Z = 3
∴ Radius of Li++ atom = `53/3 "pm" = 17.66"pm" ≈ 18 "pm"`
The given one-electron system having radius of the shortest orbit to be 18 pm may be Li++.
The given one-electron system having radius of the shortest orbit to be 18 pm may be Li++.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following curves may represent the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom as a function of trincipal quantum number n?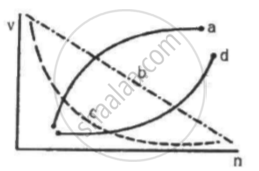
As one considers orbits with higher values of n in a hydrogen atom, the electric potential energy of the atom
Let An be the area enclosed by the nth orbit in a hydrogen atom. The graph of ln (An/A1) against ln(n)
(a) will pass through the origin
(b) will be a straight line with slope 4
(c) will be a monotonically increasing nonlinear curve
(d) will be a circle
Ionization energy of a hydrogen-like ion A is greater than that of another hydrogen-like ion B. Let r, u, E and L represent the radius of the orbit, speed of the electron, energy of the atom and orbital angular momentum of the electron respectively. In ground state
Calculate the smallest wavelength of radiation that may be emitted by (a) hydrogen, (b) He+ and (c) Li++.
Find the binding energy of a hydrogen atom in the state n = 2.
A hydrogen atom emits ultraviolet radiation of wavelength 102.5 nm. What are the quantum numbers of the states involved in the transition?
A group of hydrogen atoms are prepared in n = 4 states. List the wavelength that are emitted as the atoms make transitions and return to n = 2 states.
Find the maximum Coulomb force that can act on the electron due to the nucleus in a hydrogen atom.
Whenever a photon is emitted by hydrogen in Balmer series, it is followed by another photon in Lyman series. What wavelength does this latter photon correspond to?
What is the energy of a hydrogen atom in the first excited state if the potential energy is taken to be zero in the ground state?
Find the maximum angular speed of the electron of a hydrogen atom in a stationary orbit.
The average kinetic energy of molecules in a gas at temperature T is 1.5 kT. Find the temperature at which the average kinetic energy of the molecules of hydrogen equals the binding energy of its atoms. Will hydrogen remain in molecular from at this temperature? Take k = 8.62 × 10−5 eV K−1.
Electrons are emitted from an electron gun at almost zero velocity and are accelerated by an electric field E through a distance of 1.0 m. The electrons are now scattered by an atomic hydrogen sample in ground state. What should be the minimum value of E so that red light of wavelength 656.3 nm may be emitted by the hydrogen?
When a photon is emitted from an atom, the atom recoils. The kinetic energy of recoil and the energy of the photon come from the difference in energies between the states involved in the transition. Suppose, a hydrogen atom changes its state from n = 3 to n = 2. Calculate the fractional change in the wavelength of light emitted, due to the recoil.
In a hydrogen atom the electron moves in an orbit of radius 0.5 A° making 10 revolutions per second, the magnetic moment associated with the orbital motion of the electron will be ______.
The Balmer series for the H-atom can be observed ______.
- if we measure the frequencies of light emitted when an excited atom falls to the ground state.
- if we measure the frequencies of light emitted due to transitions between excited states and the first excited state.
- in any transition in a H-atom.
- as a sequence of frequencies with the higher frequencies getting closely packed.
Positronium is just like a H-atom with the proton replaced by the positively charged anti-particle of the electron (called the positron which is as massive as the electron). What would be the ground state energy of positronium?
A hydrogen atom makes a transition from n = 5 to n = 1 orbit. The wavelength of photon emitted is λ. The wavelength of photon emitted when it makes a transition from n = 5 to n = 2 orbit is ______.
