Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The side (in cm) of a triangle containing the right angle are 5x and 3x – 1. If the area of the triangle is 60 cm². Find the sides of the triangle.
उत्तर
Area of the right triangle ABC
= `(5x (3x - 1))/(2)`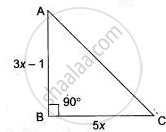
∴ `(5x (3x - 1))/(2)` = 60
⇒ 15x2 - 5x = 120
⇒ 3x2 - x = 24
⇒ 3x2 - x - 24 = 0
⇒ 3x2 - 9x + 8x - 24 = 0
⇒ 3x(x - 3) + 8(x - 3) = 0
⇒ (x - 3) (3x + 8) = 0
⇒ x - 3 = 0 or 3x + 8 = 0
⇒ x = 3 or x = `(-8)/(3)`
But x = `(-8)/(3)` is not possible as isde cannot be - ve.
Then x = 3.
Hence, sides are AB = 3x - 1 = 8 cm
BC = 5x = 15 cm
Also from AC
= `sqrt(("AB")^2 + ("BC")^2)`
= `sqrt(64 + 225)`
= `sqrt(289)`
= 17 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve (i) x2 + 3x – 18 = 0
(ii) (x – 4) (5x + 2) = 0
(iii) 2x2 + ax – a2 = 0; where ‘a’ is a real number
Solve the following quadratic equations by factorization:
6x2 - x - 2 = 0
Solve the following quadratic equations by factorization:
`sqrt2x^2-3x-2sqrt2=0`
The values of k for which the quadratic equation \[16 x^2 + 4kx + 9 = 0\] has real and equal roots are
Solve the following equation: (x-8)(x+6) = 0
The sum of the square of 2 consecutive odd positive integers is 290.Find them.
The area of right-angled triangle is 600cm2. If the base of the triangle exceeds the altitude by 10cm, find the dimensions of the triangle.
Solve equation using factorisation method:
(x + 3)2 – 4(x + 3) – 5 = 0
Solve the following equation by factorization
`(2)/(3)x^2 - (1)/(3)x` = 1
Solve the following equation by factorisation :
2x2 + ax – a2= 0
