Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV; K: 2.30 eV; Mo: 4.17 eV; Ni: 5.15 eV
Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
उत्तर
Mo and Ni will not show photoelectric emission in both cases
Wavelength for a radiation, λ = 3300 Å = 3300 × 10−10 m
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Planck’s constant, h = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
The energy of incident radiation is given as:
`"E" = "hc"/lambda`
= `(6.6 xx 10^(-34) xx 3 xx 10^8)/(3300 xx 10^(-10))`
= 6 × 10−19 J
= `(6 xx 10^(-19))/(1.6 xx 10^(-19))`
= 3.158 eV
It can be observed that the energy of the incident radiation is greater than the work function of Na and K only. It is less for Mo and Ni. Hence, Mo and Ni will not show photoelectric emission.
If the source of light is brought near the photocells and placed 50 cm away from them, then the intensity of radiation will increase. This does not affect the energy of the radiation. Hence, the result will be the same as before. However, the photoelectrons emitted from Na and K will increase in proportion to intensity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use the same formula you employ in (a) to obtain electron speed for an collector potential of 10 MV. Do you see what is wrong? In what way is the formula to be modified?
Light of intensity 10−5 W m−2 falls on a sodium photo-cell of surface area 2 cm2. Assuming that the top 5 layers of sodium absorb the incident energy, estimate time required for photoelectric emission in the wave-picture of radiation. The work function for the metal is given to be about 2 eV. What is the implication of your answer?
Draw graphs showing variation of photoelectric current with applied voltage for two incident radiations of equal frequency and different intensities. Mark the graph for the radiation of higher intensity.
Should the energy of a photon be called its kinetic energy or its internal energy?
Two photons of
Let nr and nb be the number of photons emitted by a red bulb and a blue bulb, respectively, of equal power in a given time.
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
When the sun is directly overhead, the surface of the earth receives 1.4 × 103 W m−2 of sunlight. Assume that the light is monochromatic with average wavelength 500 nm and that no light is absorbed in between the sun and the earth's surface. The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. (a) Calculate the number of photons falling per second on each square metre of earth's surface directly below the sun. (b) How many photons are there in each cubic metre near the earth's surface at any instant? (c) How many photons does the sun emit per second?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A small piece of cesium metal (φ = 1.9 eV) is kept at a distance of 20 cm from a large metal plate with a charge density of 1.0 × 10−9 C m−2 on the surface facing the cesium piece. A monochromatic light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the cesium piece. Find the minimum and maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons reaching the large metal plate. Neglect any change in electric field due to the small piece of cesium present.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
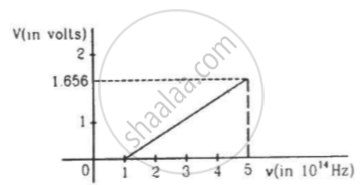
The figure is the plot of stopping potential versus the frequency of the light used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Find (a) the ratio h/e and (b) the work function.
Define the terms "stopping potential' and 'threshold frequency' in relation to the photoelectric effect. How does one determine these physical quantities using Einstein's equation?
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
- Assertion (A): For the radiation of a frequency greater than the threshold frequency, the photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation.
- Reason (R): Greater the number of energy quanta available, the greater the number of electrons absorbing the energy quanta and the greater the number of electrons coming out of the metal.
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
