Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three elements B, Si and Ge are
पर्याय
metals
non-metals
metalloids
metal, non-metal and metalloid respectively
उत्तर
metalloids
Explanation -
Out of the given options, all the elements come under the category of metalloids.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Arrange the following as per the instructions given in the brackets:
Na, K, Cl, S, Si (increasing order ionization energy)
Give the trend in metallic character:
(i) across the period left to right
Name the periodic property which relates to the character of element which loses one or more electrons when supplied with energy.
The electronic configuration of an element T is 2, 8, 8, 1.
Is it a metal or a non-metal?
Study the extract of the Periodic Table given below and answer the questions that follow. Give the alphabet corresponding to the element in question. DO NOT repeat an element. 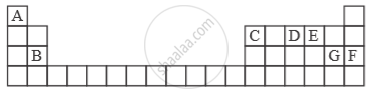
Which non-metallic element has the valency of 2?
Explain
Larger the atomic size, more metallic is the element.
Within a group, where would you expect to find the element with the greatest metallic character.
Use the information given in (a) to (h) to identify the substances P to W selecting your answers from the given list.
List:
| Calcium | Oxygen | Copper (II) Oxide |
| Carbon | Calcium hydroxide | Copper (II) Nitrate |
| Lead (II) Oxide | Hydrogen chloride | Chlorine |
| Lead (II) Nitrate | Calcium Oxide | Ammonium chloride |
- P is white solid. When heated produces white fumes (sublime).
- P and R on warming produce an alkaline gas.
- On adding water to T, heat is evolved and R is formed.
- Q burns brightly in the air to form T.
- When S is heated, it gives off brown fumes and leaves a black residue of U.
- A solution of S is formed by warming U with dilute nitric acid.
- V is a gaseous non-metallic element that reacts with hydrogen to form W.
- A solution of W will neutralize the solution of R.
Write scientific reason.
The metallic character of elements increases while going down the groups.
The metal which is hard and has a high melting point and used in filaments of electrical bulbs is ______
