Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Three immiscible liquids of densities d1 > d2 > d3 and refractive indices µ1 > µ2 > µ3 are put in a beaker. The height of each liquid column is `h/3`. A dot is made at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, find the apparent depth of the dot.
उत्तर
Coordinate convention: At the first surface (+ upward and – ve downward)
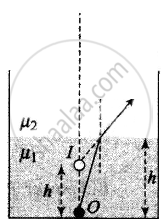
`mu_2/h^' - mu_1/(-h) = (mu_2 - mu_1)/(oo)` (infinity because the surface is plane),
or `h^' = mu_2/mu_1 h`.
The negative sign shows that it is on the side of the object
`h^'` is the apparent depth of O after refraction from the interface.

The position of image of O after refraction from surface-1. If seen from `mu_2`, the apparent depth is `h_1`
`h_1 = mu_2/mu_1 h/3`
The negative sign shows that it is on the side of the object.
Since the image formed by surface-1 will act as an object for surface-3. If seen from `mu_3`, the apparent depth is `h_2`.
Similarly, the image formed by Medium 2, O2 acts as an object for MEdium 3.
`h_2 = mu_3/mu_2 (mu_2/mu_1 h/3 + h/3) = - h/3(mu_3/mu_2 + mu_2/mu_1)`
Finally, the image formed by surface-2 will act as an object for surface-2. If seen from the outside, the apparent depth is `h_3`.
`h_3 = - 1/mu_3 [h/3 + h/3(mu_3/mu_2 + mu_3/mu_1)] = - h/3 (1/mu_1 + 1/mu_2 + 1/mu_3)`
Hence apparent depth of dot is `h/3(1/mu_1 + 1/mu_2 + 1/mu_3)`
Xa is apparent depth.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Does the apparent depth of a tank of water change if viewed obliquely? If so, does the apparent depth increase or decrease?
A fish which is at a depth of l2 em .in water `(mu = 4/3)` is viewed by an observer on the bank of a lake. Its apparent depth as observed: by the observer is:
a) 3 cm
b) 9 cm
c) 12 cm
d) 16 cm
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media A, B and C are 15°, 25° and 35° respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
Locate the image formed by refraction in the situation shown in figure.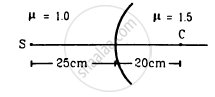
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium of refractive index n falls, on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidents of 45°. The ray can undergo total internal reflection for the following n.
What is angle of deviation due to refraction?
What is a principle of reversibility?
Obtain the equation for apparent depth.
What is Snell’s window?
An object is immersed in a fluid of refractive index 'µ'. In order that the object becomes invisible when observed from outside, it should ______.
