Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Use the correct tense form of the verb given in the bracket and rewrite the sentence.
One human should _______ this for another always.
पर्याय
done
doing
be doing
उत्तर
One human should be doing this for another always.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Change the following sentence into simple sentence.
Einstein smiled and put his arm across my shoulder.
Let us begin by studying the relationship between the different verb forms and the time they denote.
Work individually
Indicate the tense and time of each of the highlighted verbs in the table below.
The first has been done as an example.
| Sentence | Tense | Time | |
| 1. | We are planning to go out for a picnic tomorrow. | Present | Future |
| 2. | India has made tremendous progress in the past few decades. |
||
| 3. | It has been raining since morning. | ||
| 4. | Could you please send your e-mail address as soon as possible? |
||
| 5. | The train must have reached Delhi by now. |
||
| 6. | It always rains in July here. | ||
| 7. | Cold wave intensifies further. (A news headline) |
||
| 8. | He was playing here a minute ago. | ||
| 9. | She won the Student of the Year award last year. |
||
| 10. | All incomplete forms will be rejected. |
Now compare your answers with those of your partner and discuss the
following questions and write your observations in the given space.
a. Is the time referred to in the sentences always the same as the tense of
the verb? What conclusion can you draw from your observation? Write
your observation below.
...............................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................
b. How have you found the tense of the verbs in the sentences above? Are
there any indicators or markers that reveal the tense of the verb? Write
your observation below.
...............................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................
c. Did you find any verb form that could be called 'future form'? (You will
learn more about the different ways of talking about future later in this
unit.)
...............................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................
d. Why do you think verb forms are often labelled as 'simple' or 'indefinite', 'progressive' or 'continuous', 'perfect' and 'perfect continuous'?
...............................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................................
Present Progressive
(Progressive = continuous)
Form
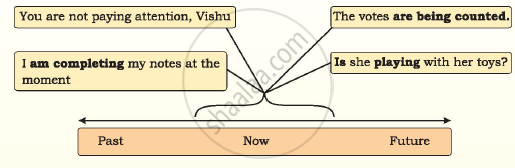
S +is/ am/ are +verb+ ing
S +is/ am/ are+ not+ verb+ ing.
Is/am/me+ S + verb+ing?
S + is/ am/ are +being+ Verb (past participle)
- Complete the following sentences by filling in the blanks with the present progressive form of the given verbs.
i. "You've put on weight, Cheryl."
"Yes. I.. .... (eat) a lot these days."
ii. "Hurry up! We ... (get) late for school."
"Justa second, please! I ... (come}."
iii. Temperatures ... (rise} all over the world.
iv. "You .... not ... (wear) this dirty shirt to office. Wait, I'll give you another."
v. "l...not ... (do) your homework-forget it. I still haven't forgotten how you
fought with me in the morning."
vi. The Prime Minister ... (leave) for Russia tomorrow on a 5 day state visit.
Vii "You ... (be) ver:yrude, Abhi."
viii. She ... always (make) excuses for coming late.
ix. Aabha ... (write) a novel these days.
- The table below shows different uses or meanings of the present progressive. Match the verbs in the above sentences with the uses or meanings they convey.
| a. Something pre-arranged or a fixed plan ............ b. Insistence............. c. Annoyance............ d. Repeated action............. e. Some development or change........... f. Emphatic refusal............. g. Something happening 'around now'.............. h. An action just starting.......... i. Temporary action not necessarily taking place at the moment of speaking............ |
*It is a little difficult to match the sentences with uses of present progressive
tense. Here are the answers:
a-vi, b-iv, c-vii, d-i, e-iii, f-v, g-ix, h-ii, i-viii.
Compare your answers with these and have a class discussion.
Verbs that are normally NOT used in the progressive form.
1. Which sentence in each of the following pairs is acceptable and
why?
1. a. I am respecting you.
b. I respect you.
2. a. My son loves to draw and paint.
b. My son is loving to draw and paint.
3. a. We are having two cars.
b. We have two cars.
4. a. I am thinking you are new to this place.
b. I think you are new to this place.
5. a. The cake smells good.
b. The cake is smelling good.
| Verbs referring to mental states (eg. know, think, believe etc) and to the use of the senses (eg. smell, taste etc) are never, or hardly ever, used in progressive forms. Some of these verbs are: believe prefer know suppose feel sound (dis)like love realise understand hear taste see hate recognise want see belong doubt imagme remember wish smell agree possess own owe involve include depend |
Can you explain the difference between?
1. a. l justcan'timaginehowyougotintosuchamess.
b. You're imagining things nothing will happen.
2. a. The coffee tastes bitter
b. Mother is tasting coffee to check ifit is too bitter.
3. a. My teacher admires my art work
b. She is admiring the latest painting I have made.
4. a. The doctor is feeling the patient's pulse.
b. The patient is feeling better.
Complete the following sentences with the appropriate forms of the given verbs.
1. Every day I(go) to school in a bus but today I (go) by car because the bus operators are on strike.
2. "Baichung Bhutia (pass) the ball to Bannerjee; Bannerjee (take) a shot at the goal but it (be) way above the goal post. The Indians (attack) much more now ... "
3. I (think) you (make) a mistake by signing this contract.
4. The doctor (say) mother (respond) to the treatment well.
5. Farzana (be) not well. She (not come) to school today.
Present Perfect vs. Simple Past
b. What conclusion can you draw from these sentences about the use of present perfect and simple past forms of verbs?
-----------------------------------
-----------------------------------
-----------------------------------
Study the following picture carefully and then write a paragraph to describe what is happening.

Look at the incomplete sentences below. Using the information provided, complete each sentence using a suitable tense. Follow the examples:
1947 until now India I has been (be) independent since 1947.
1947 India became (become) independent in 1947.
1. 1947 until now l There --------- (be) manywars.
2. 1991 There ------- (be) a war in the Persian Gulf.
3. 1953 -------- Edmund Hilary and Tensing first (climb) Everest.
4. 1953 until now Many people ________ (climb)Everest.
5. 1983 India --------- (win) the Prudential Cricket World Cup in England.
6. 1983 until now India -------- (win) many limited-overs cricket trophies.
What has been the situation of your village/town/city five to ten years ago and how has it changed since then? Write a short paragraph describing the changes in its size, population, traftlc, buildings, lifestyle etc. Which verb forms would you mainly use to describe the changes? (Hint: Simple Past and Present Perfect forms.)
Complete the following sentences correctly by using the simple past or
past perfect forms of the given verbs.
1) We ____ already (reach) home when Irlan __ (say) that he (forget) his books at school.
2) Wendy (wake up) late, then she ____ (miss) her school bus, so by the time she (reach) school, it already (start).
3) I ___ (visit) my town again ten years after I _____ (leave) it and ___ (find) thatit completely (change).
4) When Feroze and Mehr (meet) for the first time, they ___ _ (not like) each other but now they are married.
Find the incorrect sentences and then rewrite them correctly. Put a tick mark (✓)against the sentences that you think are correct.
1) By 2005, the singer recorded ten albums.
2) When I got to the bank, it had closed.
3) Timothy, the tiger, had killed five calves yesterday.
4) When Rehman met Mini ten years later, she grew up into a young girl.
5) By the time we reached the airport, the flight had left.
6) We hardly went a kilometre or so when the car broke down.
Carefully study each of the following events or situations described in a set of three sentences/phrases. Then, write a short paragraph to describe each event/situation as shown in the example. Your paragraph should begin with the description of the second event in each case. Use the verb form had+ past participle to describe the earliest of the past events.
|
• Somebody burgled the office on Sunday night. • Our arrival at work on Monday morning . • Police informed |
We arrived at work on Monday and found that somebody had burgled the office the previous night. So, we immediately informed the police. |
|
• (I) Mayank went out with his family. (ii) I tried to phone him this morning. (iii) His servant answered. |
I tried to phone Mayank this morning but the servant ........................................... ........................................... |
|
• (i) Rohit returned from holiday.(ii) Jayanti met Rohit. |
Jayanti met Rohit, who ........................................... ........................................... |
|
• (I) All the arrangements were finalised for the seminar. (ii) The seminar participants arrived in Gangtok. (iii) Met the professors from the UK the same evening. |
The participants arrived in Gangtok. They found ........................................... ........................................... |
Now write short paragraphs to describe the trends in the other groups of visitors featured in the graph.
• Overseas Visitors
....................................................
....................................................
• Domestic Visitors
....................................................
....................................................
• Total Number ofVisitors
....................................................
....................................................
Working with the same partner, use the information given below and
discuss the reasons for choosing a particular verb form in F .1. Then match
the information in the bubbles below with the sentences, and put the
sentence number in the space provided, as shown in the example.
| 1. e.g. Something is expected to happen before a particular time in the future. (Sentence No 2) |
2.Statement of a universal truth or fact. ( ) |
|
3.Something is expected to ( ) |
4.Simple statement of future ( ) |
|
5.Sure to happen at a particular time in the future, as arrangements for it ( ) |
6.Statement of a planned event expected. ( } |
The Dauphin will give me all I need.
(Rewrite the sentence using the present perfect tense)
Read this sentence.
M. Hamel had said that he would question us on participles.
In the sentence above, the verb form “had said” in the first part is used to indicate an “earlier past.” The whole story is narrated in the past. M. Hamel’s “saying” happened earlier than the events in this story. This form of the verb is called the past perfect.
Pick out five sentences from the story with this form of verb and say why this form has been used.
Use the correct tense form of the verb given in the bracket and rewrite the sentence.
She ________ that old fashion book of her mother a few months back.
Use the correct tense form of the verb given in the bracket and rewrite the sentence.
All this ________ destroyed in a few years.
Use the correct tense form of the verb given in the bracket and rewrite the sentence.
She ______ like a dressmaker’s dummy standing there.
Name the Tense of the Verb underlined to include Time (Past/Present/Future) and Aspect (Simple/Continuous/Perfect/Perfect Continuous).
I slept on the floor.
Name the Tense of the Verb underlined to include Time (Past/Present/Future) and Aspect (Simple/Continuous/Perfect/Perfect Continuous).
You haven’t found it.
Name the Tense of the Verb underlined to include Time (Past/Present/Future) and Aspect (Simple/Continuous/Perfect/Perfect Continuous).
It had made all the difference.
Name the Tense of the Verb underlined to include Time (Past/Present/Future) and Aspect (Simple/Continuous/Perfect/Perfect Continuous).
I am fine, now.
Name the Tense of the Verb underlined to include Time (Past/Present/Future) and Aspect (Simple/Continuous/Perfect/Perfect Continuous).
I have been facing death.
Change the Tense as instructed.
Life hits you in the head. (Present Perfect Continuous)
Change the Tense as instructed.
The dots will somehow connect. (Past Perfect)
Rewrite the sentence as per the instruction given along with it.
The mother langur looked straight into my eyes.
(Rewrite the sentence in the Simple Present Tense)
Rewrite the sentence as per the instruction given along with it.
She surveyed the area for the vicious male langur.
(Rewrite the sentence in the Simple Future Tense)
Rewrite the sentence as per the instruction given along with it.
She simply sat there quietly.
(Rewrite the sentence in the Present Continuous Tense)
Underline the verb and choose the correct option from the options.
They are sportsmen.
Read the following sentence carefully, underline the verb and find out the tense in the sentence.
She is standing on a little high hump on the plateau.
Read the following sentence carefully, underline the verb and find out the tense in the sentence.
He leaned out eagerly.
Match the sentences given in part ‘A’ with the sentences given in part ‘B’. Note the differences in structure.
| ‘A’ Part | B’ Part |
| (1) He was kidnapped by an extremist militia. | (a) They forced the child to kill his friends and family |
| (2) The child was forced to kill his friends and family. | (b) An extremist militia kidnapped him. |
Observe the following underlined phrases. Here ‘have /has’ are followed by the past participle form of the verb. This construction indicates the perfect present tense. Find more such sentences from the speech.
- We have made progress in the last couple of decades.
- We have prevented millions of child deaths.
- It has happened.
- ________________________
- ________________________
- ________________________
Rewrite in the past perfect continuous tense:
The marlin fights for its life desperately.
Rewrite the sentence in future tense:
I am doing it.
Rewrite the sentence in simple future tense.
He has been playing since afternoon.
Rewrite the sentence in the simple present tense.
He will go to the school.
Fill in each of the numbered blanks with the correct form of the word given in brackets. Do not copy the passage but write in correct serial order the word or phrase appropriate to the blank space.
It was hot in the railway compartment and the fan ______ (1) (not work). The elderly lady ______ (2) (use) up all her water because she had cheerfully shared it with her fellow passengers. She knew that the train ______ (3) (halt) at the station for only three minutes. Calling a shoeshine boy she said, ‘Will you help me? I ______ (4) (need) a bottle of cold water and here is the money,' and she put a twenty rupee note in his hand. The boy snatched the money and ______ (5) (disappear) into the crowd on the platform. A fellow passenger ______ (6) (cannot believe) what he had witnessed. ‘What ______ (7) (you do)?’ He said, ‘You ______ (8) (never see) your money again.' Just then the whistle was heard and the train began to move. At that moment the child appeared at the window with the water. 'Your water,' he gasped, out of breath. ‘And the change.'
