Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
उत्तर
The secondary structure of protein refers to the shape in which a long polypeptide chain can exist. They are found to exist in two different types of structures, viz., an α-helix and a β-pleated sheet structure. These structures arise due to the regular folding of the backbone of the polypeptide chain due to hydrogen bonding between \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{O}\\||\\\ce{-C-}\end{array}\] and –NH– groups of the peptide bond.
α-Helix is one of the most common ways in which a polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right handed screw (helix) with the –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen bonded to the \[\begin{array}{cc}\backslash\phantom{.....}\\\ce{C=O}\\/\phantom{......}\end{array}\] of an adjacent turn of the helix as shown in the figure.
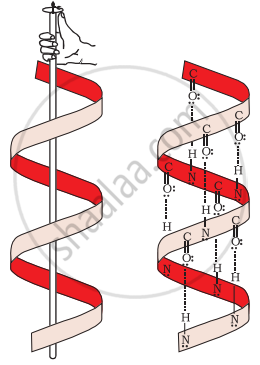
α-Helix structure of proteins
In β-pleated sheet structure, all peptide chains are stretched out to nearly maximum extension and then laid side by side, which are held together by intermolecular hydrogen bonds. The structure resembles the pleated folds of drapery and therefore is known as a β-pleated sheet.
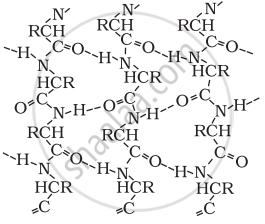
β-Pleated sheet structure of proteins
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following as related to proteins:
Peptide linkage
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
Which of the following statement is correct:
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 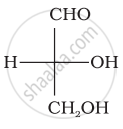 |
| (II) | 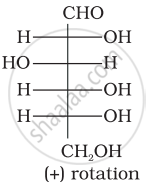 |
| (III) | 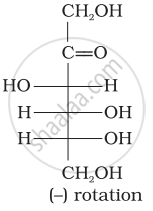 |
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Peptide linkage is:
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Out of the following, which type of interaction is responsible for the stabilisation of the α-helix structure of proteins?
The correct structure of Ruhemann's Purple, the compound formed in the reaction of ninhydrin with proteins is:
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
An α-helix is a structural feature of ______.
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Write a classification of proteins with an example.
