Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
उत्तर
The forces intersect (or) passing through the axis of rotation cannot produce torque as the perpendicular distance between the forces is 0 i.e. r = 0.
∴ `vectau = vecr xx vecF = 0`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the resultant torque of all the forces acting on a body is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will be zero about any other point?
A body is in translational equilibrium under the action of coplanar forces. If the torque of these forces is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will also be zero about any other point?
When a body is weighed on an ordinary balance we demand that the arum should be horizontal if the weights on the two pans are equal. Suppose equal weights are put on the two pans, the arm is kept at an angle with the horizontal and released. Is the torque of the two weights about the middle point (point of support) zero? Is the total torque zero? If so, why does the arm rotate and finally become horizontal?
A particle of mass m is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal. Find the torque of the weight of the particle about the point of projection when the particle is at the highest point.
A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle θ with the vertical. Find the magnitude of the torque of the weight ω of the bob about the point of suspension. When is the torque zero?
A cubical block of mass m and edge a slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with a uniform speed. Find the torque of the normal force acting on the block about its centre.
A 6⋅5 m long ladder rests against a vertical wall reaching a height of 6⋅0 m. A 60 kg man stands half way up the ladder.
- Find the torque of the force exerted by the man on the ladder about the upper end of the ladder.
- Assuming the weight of the ladder to be negligible as compared to the man and assuming the wall to be smooth, find the force exerted by the ground on the ladder.
A particle of mass 5 units is moving with a uniform speed of v = `3sqrt 2` units in the XOY plane along the line y = x + 4. Find the magnitude of angular momentum
Figure shows two identical particles 1 and 2, each of mass m, moving in opposite directions with same speed v along parallel lines. At a particular instant, r1 and r2 are their respective position vectors drawn from point A which is in the plane of the parallel lines. Choose the correct options:
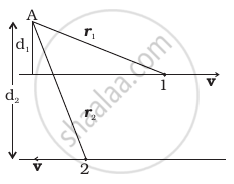
- Angular momentum l1 of particle 1 about A is l1 = mvd1
- Angular momentum l2 of particle 2 about A is l2 = mvr2
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv(r1 + r2)
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv (d2 − d1)
⊗ represents a unit vector coming out of the page.
⊗ represents a unit vector going into the page.
The position vector of 1 kg object is `vecr = (3hati - hatj)` m and its velocity `vecv = (3hati + hatk)` ms-1. The magnitude of its angular momentum is `sqrtx` Nm where x is ______.
