Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose?
उत्तर
Lactose is composed of β-D galactose and β-D glucose. On hydrolysis, it gives two molecules of lactose monosaccharide, i.e., one molecule each of D-(+)-glucose and D-(+)-galactose.
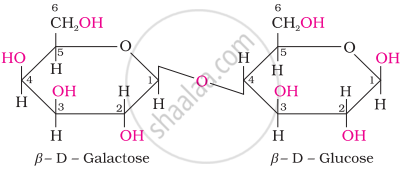
\[\ce{\underset{Lactose}{C12H22O11} + H2O ->[H3O+][or Lactose] \underset{D-(+)-glucose}{C6H12O6} + \underset{D-(+)-galactose}{C6H12O6}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
What are reducing sugars?
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose
Which of the following gives a positive Fehling solution test?
Glucose gives silver mirror test with Tollen’s reagent. It shows the presence of ____________.
The two functional groups present in a typical carbohydrate are:
Monosaccharides usually contains ____________ carbon atoms.
A carbohydrate that cannot be hydrolysed into simpler units is called ____________.
The pair of compounds in which both the compounds give the positive test with Tollen’s reagent is:
Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.

Which of the following monosaccharides are present as five membered cyclic structure (furanose structure)?
(i) Ribose
(ii) Glucose
(iii) Fructose
(iv) Galactose
Name the sugar present in milk. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? What are such oligosaccharides called?
Name the linkage connecting monosaccharide units in polysaccharides.
What are glycosidic linkages? In which type of biomolecules are they present?
Assertion: Deoxyribose, \[\ce{C5H10O4}\] is not a carbohydrate.
Reason: Carbohydrates are hydrates of carbon so compounds which follow \[\ce{C_x(H2O)_y}\] formula are carbohydrates.
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. They are also called saccharides. All those carbohydrates which reduce Fehling's solution and Tollen's reagent are referred to as reducing sugars. Glucose, the most important source of energy for mammals, is obtained by the hydrolysis of starch. Vitamins are accessory food factors required in the diet. Proteins are the polymers of α-amino acids and perform various structural and dynamic functions in the organisms. Deficiency of vitamins leads to many diseases. |
Answer the following:
(a) The penta-acetate of glucose does not react with Hydroxylamine. What does it indicate? (1)
(b) Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body? (1)
(c) Define the following as related to proteins: (2)
- Peptide linkage
- Denaturation
OR
(c) Define the following as related to carbohydrates: (2)
- Anomers
- Glycosidic linkage
