Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens when (CH3)3 C – OH is heated with Cu/573 K?
Write the chemical equation in support of your answer.
उत्तर
When a tertiary alcohol is heated with Copper at 573 K, due to absence of α-hydrogen atom dehydration reaction takes place and produce 2-methyl propene.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{.....................}|\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - C - OH ->[Cu][573K] \underset{2-metyl propene}{CH3 - C = CH2}}\\
|\phantom{......................}\\
\ce{\underset{Tertiary Butanol}{CH3}}\phantom{...................}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
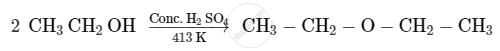
Cyclohexene is best prepared from cyclohexanol by which of the following:
Identify the secondary alcohols from the following set:
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3}\]
- \[\ce{(C2H5)3COH}\]
Assertion: Bond angle in ethers is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
Reason: There is a repulsion between the two bulky (–R) groups.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
