Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is meant by positive and negative deviations from Raoult's law and how is the sign of ΔmixH related to positive and negative deviations from Raoult's law?
उत्तर
According to Raoult’s law, the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in any solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction. The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions. If the solution does not obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration, then it is called a non-ideal solution. The vapour pressure of such a solution is either higher or lower than that predicted by Raoult’s law. If the vapour pressure is higher, then the solution is said to exhibit a positive deviation, and if it is lower, then the solution is said to exhibit a negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
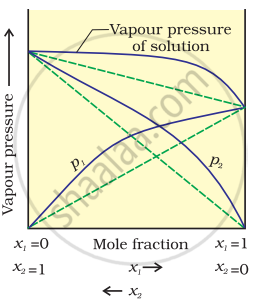
Vapour pressure of a two-component solution shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
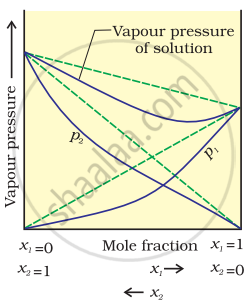
Vapour pressure of a two-component solution shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law
In the case of an ideal solution, the enthalpy of mixing the pure components to form the solution is zero.
ΔmixH = 0
In the case of solutions showing positive deviations, absorption of heat takes place.
∴ ΔmixH = Positive
In the case of solutions showing negative deviations, the evolution of heat takes place.
∴ ΔmixH = Negative
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components are 105.2 kPa and 46.8 kPa respectively. What will be the vapour pressure of a mixture of 26.0 g of heptane and 35 g of octane?
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
acetonitrile (CH3CN) and acetone (C3H6O)
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
Ideal solutions obey ………. law and they …………. form azeotropic mixtures.
(Henry’s, aldol condensation, absence, do not, ohm, Raoult’s, increases, common ion effect, easily, three, solubility product, ohm-1, two, four, ohm-1, cm2, Cannizzaro, ohm-1 cm-1, zero, decreases, presence)
The molality of a solution containing 1.8 g of glucose dissolved in 250 g of water is
The KH for the solution of oxygen dissolved in water is 4 × 104 atm at a given temperature. If the partial pressure of oxygen in air is 0.4 atm, the mole fraction of oxygen in solution is ______.
The mass of a non – volatile solute (molar mass 80 g mol-1) should be dissolved in 92g of toluene to reduce its vapour pressure to 90% ______.
Assertion: An ideal solution obeys Raoults Law.
Reason: In an ideal solution, solvent – solvent as well as solute – solute interactions are similar to solute-solvent interactions.
For ideal solution the volume of mixing of the pure components to form the solution is ____________.
Which of the following condition is not satisfied by an ideal solution?
Which relationship is not correct?
If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then ______.
Assertion: Molarity of a solution in liquid state changes with temperature.
Reason: The volume of a solution changes with change in temperature.
Explain the terms ideal and non-ideal solutions in the light of forces of interactions operating between molecules in liquid solutions.
The pH of a solution of hydrochloric acid is 1.5. Calculate the concentration of the acid.
Lowering of vapour pressure of an aqueous solution of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte 1 molal aqueous solution at 100°C is ______.
Assertion (A): The enthalpy of mixing Δmix H is equal to zero for an ideal solution.
Reason (R): For an ideal solution the interaction between solute and solvent molecules is stronger than the interactions between solute-solute or solvent-solvent molecules.
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
NaClO4 and water
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
methanol and acetone
