Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is meant by positive and negative deviations from Raoult's law and how is the sign of ΔmixH related to positive and negative deviations from Raoult's law?
Solution
According to Raoult’s law, the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in any solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction. The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions. If the solution does not obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration, then it is called a non-ideal solution. The vapour pressure of such a solution is either higher or lower than that predicted by Raoult’s law. If the vapour pressure is higher, then the solution is said to exhibit a positive deviation, and if it is lower, then the solution is said to exhibit a negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
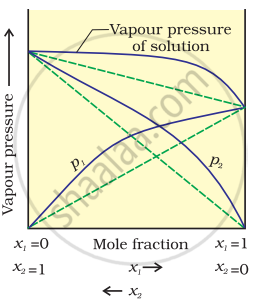
Vapour pressure of a two-component solution shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
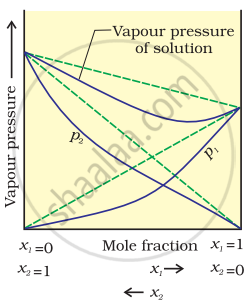
Vapour pressure of a two-component solution shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law
In the case of an ideal solution, the enthalpy of mixing the pure components to form the solution is zero.
ΔmixH = 0
In the case of solutions showing positive deviations, absorption of heat takes place.
∴ ΔmixH = Positive
In the case of solutions showing negative deviations, the evolution of heat takes place.
∴ ΔmixH = Negative
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components are 105.2 kPa and 46.8 kPa respectively. What will be the vapour pressure of a mixture of 26.0 g of heptane and 35 g of octane?
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
acetonitrile (CH3CN) and acetone (C3H6O)
What type of intermolecular attractive interaction exists in the pair of methanol and acetone?
The molality of a solution containing 1.8 g of glucose dissolved in 250 g of water is
Which of the following concentration terms is/are independent of temperature
Which one of the following is incorrect for an ideal solution?
Two liquids X and Y on mixing gives a warm solution. The solution is ______.
The mass of a non – volatile solute (molar mass 80 g mol-1) should be dissolved in 92g of toluene to reduce its vapour pressure to 90% ______.
Which relationship is not correct?
Which of the following is an example of a solid solution?
If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then ______.
Concentration terms such as mass percentage, ppm, mole fraction and molality are independent of temperature, however molarity is a function of temperature. Explain.
Why soda water bottle kept at room temperature fizzes on opening?
Dissociation constant and molar conductance of an acetic acid solution are 1.78 × 10–5 mol L–1 and 48.15 S cm–2 mol–1 respectively. The conductivity of the solution is (considering molar conductance at infinite dilution is 390.5 S cm–2 mol–1)
On increase in pressure for dissociation ofN2O4 into NO2, equilibrium shift towards
Assertion (A): The enthalpy of mixing Δmix H is equal to zero for an ideal solution.
Reason (R): For an ideal solution the interaction between solute and solvent molecules is stronger than the interactions between solute-solute or solvent-solvent molecules.
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
n-hexane and n-octane
