Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom ______.
पर्याय
do not change for any type of radioactivity.
change for α and β radioactivity but not for γ-radioactivity.
change for α-radioactivity but not for others.
change for β-radioactivity but not for others.
उत्तर
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom change for α and β radioactivity but not for γ-radioactivity.
Explanation:
| Features | α- particles | β- particles | γ-rays | |
| 1. | Identity | Helium nucleus or doubly ionised helium atom (2He4) | Fast moving electron (–β0 or B–) |
Photons (E.M. waves) |
| 2. | Charge | + 2e | – e | Zero |
| 3. | Mass | 4 mp (mp = mass of proton) = 1.87 × 10–27 |
me | Massless |
| 4. | Equation of decay |
\[\ce{_{Z}X^A ->[α-decay]}\] \[\ce{_{z-2}Y^{A-4} + _{2}He^4}\] \[\ce{n_α = A - A^{'}/4}\] |
\[\ce{_{z}X^A -> _{z + 1} Y^A + _{-1}e^0 + {v}}\] \[\ce{_{z}y^A ->[n_{β}] z^' X^A}\] ⇒ nβ = (2nα = – Z + Z') |
\[\ce{_{Z}X^A -> _{Z}X^α + γ}\] |
A /3-particle carries one unit of negative charge (– e), an α-particle carries 2 units of positive charge (+ 2e) and γ (particle) carries no charge. Hence electronic energy levels of the atom charge for α and β decay, but not for γ-decay.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How is the mean life of a given radioactive nucleus related to the decay constant?
Using the equation `N = N_0e^(-lambdat)` obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (`lambda`) of a radioactive substance.
The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence
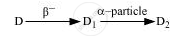
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is (i) the mass number (ii) atomic number of D?
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
Lithium (Z = 3) has two stable isotopes 6Li and 7Li. When neutrons are bombarded on lithium sample, electrons and α-particles are ejected. Write down the nuclear process taking place.
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
Obtain an expression for the decay law of radioactivity. Hence show that the activity A(t) =λNO e-λt.
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
