Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence
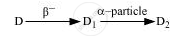
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is (i) the mass number (ii) atomic number of D?
उत्तर
An alpha (α) particle is a helium nucleus (`""_2^4He)`and a beta-minus decay (β−) is an emission of an electron.
The substance D2 can be represented as `""_71^176D_2`.
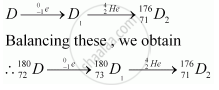
Hence,
(i) The mass number of D is 180.
(ii) The atomic number of D is 72.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
(a) Derive the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive substance.
(b) A radioactive element reduces to 25% of its initial mass in 1000 years. Find its half life.
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
Lithium (Z = 3) has two stable isotopes 6Li and 7Li. When neutrons are bombarded on lithium sample, electrons and α-particles are ejected. Write down the nuclear process taking place.
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the production of the radioactive isotope starts at t = 0. Find the number of active nuclei at time t.
Identify the nature of the radioactive radiations emitted in each step of the decay process given below.
`""_Z^A X -> _Z^A _-1^-4 Y ->_Z^A _-1^-4 W`
A source contains two species of phosphorous nuclei, \[\ce{_15^32P}\] (T1/2 = 14.3 d) and \[\ce{_15^33P}\] (T1/2 = 25.3 d). At time t = 0, 90% of the decays are from \[\ce{_15^32P}\]. How much time has to elapse for only 15% of the decays to be from \[\ce{_15^32P}\]?
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?