Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
पर्याय
a and c
a and d
b and d
a and b
उत्तर
b and d
Explanation:
Law of radioactive disintegration: According to Rutherford and Soddy law for radioactive decay is as follows:
At any instant, the rate of decay of radioactive atoms is proportional to the number of atoms present at that instant.” i.e.
dN/dt ∞ N ⇒ dN/dt = – λN
it can be proved that N = N0e–λ1
In terms of mass M – M0e–λ1
where N = Number of atoms that remain undecayed after time t,
N0 = Number of atoms present initially (i.e., at t = 0),
M = Mass of radioactive nuclei at time t,
M0 = Mass ofradioactive nuclei at time t = 0,
N0 – N= Number of the disintegrated nuclei in time t,
dN/dt= rate of decay, λ = Decay constant or disintegration constant or radioactivity constant or Rutherford Soddy’s constant or the probability of decay per unit time of a nucleus.
The samples of the two radioactive nuclides A and B can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time if the initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
Also, when the initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive `""_6^14"C"` present with the stable carbon isotope `""_6^12"C"`. When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of `""_6^14"C"` and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of `""_6^14"C"` dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjodaro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation.
A source contains two phosphorous radio nuclides `""_15^32"P"` (T1/2 = 14.3d) and `""_15^33"P"` (T1/2 = 25.3d). Initially, 10% of the decays come from `""_15^33"P"`. How long one must wait until 90% do so?
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
Define one Becquerel.
Disintegration rate of a sample is 1010 per hour at 20 hours from the start. It reduces to 6.3 x 109 per hour after 30 hours. Calculate its half-life and the initial number of radioactive atoms in the sample.
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom ______.
The variation of decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in figure.
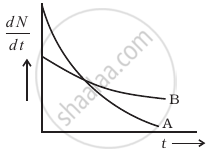
Which of the following statements are true?
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A.
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B but it does not always decay faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is smaller than that of A but still its decay rate becomes equal to that of A at a later instant.
