Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
उत्तर
Given:
Decay constant, `lambda = 4.9 xx 10^-18 "s"^-1`
(a) Average life of uranium (`tau`) is given by
`tau = 1/lambda`
= `1/(4.9 xx 10^-18)`
= `1/4.9 xx 10^18 "s"`
= `10^16/(4.9 xx 365 xx 24 xx 36) "years"`
= `10^16/(4.9 xx 365 xx 24 xx 36) "years"`
= `6.47 xx 10^-7 xx 10^16 "years"`
= `6.47 xx 10^9 "years"`
(b) Half-life of uranium (`T_"1/2"`) is given by
`T_"1/2" = 0.693/lambda = 0.693/(4.9 xx 10^-18)`
= `0.693/4.9 xx 10^18 "s"`
= `0.1414 xx 10^18 "s"`
= `(0.1414 xx 10^18)/(365 xx 24 xx 3600)`
= `(1414 xx 10^12)/(365 xx 24 xx 36)`
= `4.48 xx 10^-3 xx 10^12`
= `4.5 xx 10^9` years
(c) Time, t = 9 × 109 years
Activity (A) of the sample, at any time t, is given by
`A = A_0/2^(t/T_"1/2")`
Here , `A_0` = Activity of the sample at t = 0
`therefore A_0/A = 2^((9 xx 10^9)/(4.5 xx 10^9)) = 2^2 = 4`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the law of radioactive decay.
How is the mean life of a given radioactive nucleus related to the decay constant?
Write symbolically the process expressing the β+ decay of `""_11^22Na`. Also write the basic nuclear process underlying this decay.
The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive `""_6^14"C"` present with the stable carbon isotope `""_6^12"C"`. When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of `""_6^14"C"` and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of `""_6^14"C"` dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjodaro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation.
The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by
Q = [mA+ mb − mC − md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^12_6C + ^12_6C ->^20_10Ne + ^4_2He}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12C)` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
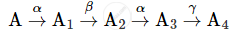
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
Define the activity of a given radioactive substance. Write its S.I. unit.
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
The half-life of 40K is 1.30 × 109 y. A sample of 1.00 g of pure KCI gives 160 counts s−1. Calculate the relative abundance of 40K (fraction of 40K present) in natural potassium.
What is the amount of \[\ce{_27^60Co}\] necessary to provide a radioactive source of strength 10.0 mCi, its half-life being 5.3 years?
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
Before the year 1900 the activity per unit mass of atmospheric carbon due to the presence of 14C averaged about 0.255 Bq per gram of carbon.
(a) What fraction of carbon atoms were 14C?
(b) An archaeological specimen containing 500 mg of carbon, shows 174 decays in one hour. What is the age of the specimen, assuming that its activity per unit mass of carbon when the specimen died was equal to the average value of the air? The half-life of 14C is 5730 years.
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
Which one of the following nuclei has shorter meant life?
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
The variation of decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in figure.
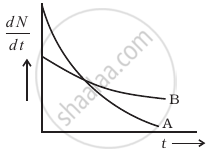
Which of the following statements are true?
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A.
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B but it does not always decay faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is smaller than that of A but still its decay rate becomes equal to that of A at a later instant.
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 14C activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 14C activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given half-life of 14C is 5760 years.
What is the half-life period of a radioactive material if its activity drops to 1/16th of its initial value of 30 years?
