Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
उत्तर
Data: T1/2 = 272 d = 272 × 24 × 60 × 60s = 2.35 × 107 s, A0 = 2.0 µCi= 2.0 × 10-6 × 3.7 × 1010 = 7.4 × 104 dis/s
t = 1 year = 3.156 × 107 s
(a) `"T"_(1//2) = 0.693/lambda = 0.693 tau`
∴ The mean lifetime for 57Co =
`tau = "T"_(1//2)/0.693 = (2.35 xx 10^7)/0.693 = 3.391 xx 10^7`s
The decay constant for 57Co = `lambda = 1/tau`
`= 1/(3.391 xx 10^7"s")`
= 2.949 × 10-8 s-1
(b) `"A"_0 = "N"_0lambda`
∴ `"N"_0 = "A"_0/lambda = "A"_0tau`
`= (7.4 xx 10^4)(3.391 xx 10^7)`
= 2.509 × 1012 nuclei
(c) A(t) = `"A"_0"e"^(-lambda"t") = "2e"^(-(2.949 xx 10^-8)(3.156 xx 10^7))`
`= 2"e"^(-0.9307) = 2//"e"^0.9307`
Let x = `"e"^(0.9307)`
∴ logex = 0.9307
∴ 2.303 log10x = 0.9307
∴ `log_10"x" = 0.9307/2.303 = 0.4041`
∴ x = antilog 0.4041=2.536
∴ A(t) = `2/2.536 mu"Ci" = 0.7886 mu`Ci
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Write the basic nuclear process involved in the emission of β+ in a symbolic form, by a radioactive nucleus.
(b) In the reactions given below:
(i)`""_16^11C->_y^zB+x+v`
(ii)`""_6^12C+_6^12C->_a^20 Ne + _b^c He`
Find the values of x, y, and z and a, b and c.
State the law of radioactive decay.
Derive the mathematical expression for law of radioactive decay for a sample of a radioactive nucleus
How is the mean life of a given radioactive nucleus related to the decay constant?
Obtain the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive sample.
Write symbolically the process expressing the β+ decay of `""_11^22Na`. Also write the basic nuclear process underlying this decay.
Why is it found experimentally difficult to detect neutrinos in nuclear β-decay?
Obtain the amount of `""_27^60"Co"` necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8.0 mCi strength. The half-life of `""_27^60"Co"` is 5.3 years.
The half-life of `""_38^90 "Sr"` is 28 years. What is the disintegration rate of 15 mg of this isotope?
The radionuclide 11C decays according to
\[\ce{^11_6C -> ^11_5B + e+ + \text{v}}\] : T1/2 = 20.3 min
The maximum energy of the emitted positron is 0.960 MeV.
Given the mass values: `"m"(""_6^11"C") = 11.011434 u and "m"(""_6^11"B") = 11.009305 "u"`
Calculate Q and compare it with the maximum energy of the positron emitted.
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by
Q = [mA+ mb − mC − md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^12_6C + ^12_6C ->^20_10Ne + ^4_2He}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12C)` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
A source contains two phosphorous radio nuclides `""_15^32"P"` (T1/2 = 14.3d) and `""_15^33"P"` (T1/2 = 25.3d). Initially, 10% of the decays come from `""_15^33"P"`. How long one must wait until 90% do so?
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
Represent Radioactive Decay curve using relation `N = N_o e^(-lambdat)` graphically
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
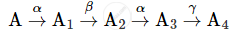
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Using the equation `N = N_0e^(-lambdat)` obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (`lambda`) of a radioactive substance.
(a) Derive the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive substance.
(b) A radioactive element reduces to 25% of its initial mass in 1000 years. Find its half life.
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
In a radioactive decay, neither the atomic number nor the mass number changes. Which of the following particles is emitted in the decay?
A freshly prepared radioactive source of half-life 2 h emits radiation of intensity which is 64 times the permissible safe level. The minimum time after which it would be possible to work safely with this source is
Lithium (Z = 3) has two stable isotopes 6Li and 7Li. When neutrons are bombarded on lithium sample, electrons and α-particles are ejected. Write down the nuclear process taking place.
The masses of 11C and 11B are respectively 11.0114 u and 11.0093 u. Find the maximum energy a positron can have in the β*-decay of 11C to 11B.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
28Th emits an alpha particle to reduce to 224Ra. Calculate the kinetic energy of the alpha particle emitted in the following decay:
`""^228"Th" → ""^224"Ra"^(∗) + alpha`
`""^224"Ra"^(∗) → ""^224"Ra" + γ (217 "keV")`.
Atomic mass of 228Th is 228.028726 u, that of 224Ra is 224.020196 u and that of `""_2^4H` is 4.00260 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
57Co decays to 57Fe by β+- emission. The resulting 57Fe is in its excited state and comes to the ground state by emitting γ-rays. The half-life of β+- decay is 270 days and that of the γ-emissions is 10−8 s. A sample of 57Co gives 5.0 × 109 gamma rays per second. How much time will elapse before the emission rate of gamma rays drops to 2.5 × 109per second?
When charcoal is prepared from a living tree, it shows a disintegration rate of 15.3 disintegrations of 14C per gram per minute. A sample from an ancient piece of charcoal shows 14C activity to be 12.3 disintegrations per gram per minute. How old is this sample? Half-life of 14C is 5730 y.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the production of the radioactive isotope starts at t = 0. Find the number of active nuclei at time t.
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
A radioactive substance disintegrates into two types of daughter nuclei, one type with disintegration constant λ1 and the other type with disintegration constant λ2 . Determine the half-life of the radioactive substance.
What is the amount of \[\ce{_27^60Co}\] necessary to provide a radioactive source of strength 10.0 mCi, its half-life being 5.3 years?
Obtain an expression for the decay law of radioactivity. Hence show that the activity A(t) =λNO e-λt.
A radioactive element disintegrates for an interval of time equal to its mean lifetime. The fraction that has disintegrated is ______
Which one of the following nuclei has shorter meant life?
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
After 1 hour, `(1/8)^"th"` of the initial mass of a certain radioactive isotope remains undecayed. The half-life of the isotopes is ______.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom ______.
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
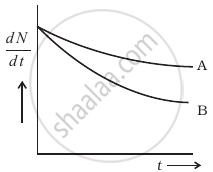
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
The radioactivity of an old sample of whisky due to tritium (half-life 12.5 years) was found to be only about 4% of that measured in a recently purchased bottle marked 10 years old. The age of a sample is ______ years.
