Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
उत्तर
Given:-
Atomic mass of 12N, m(12N) = 12.018613 u
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43 MeV)
Net reaction is given by
12N → 12C + e+ + v + γ (4.43 MeV)
Qvalue of the `β^+` decay will be
Qvalue = [m(`""^12N`) - (m(12C*) + 2me)]c2
`= [12.018613 xx 931 "MeV" - (12 xx 931 + 4.43) "MeV" - (2 xx 511) "keV"]`
= [11189.3287 - 11176.43 - 1.022] MeV
`= 11.8767 "MeV" = 11.88 "MeV"`
The maximum kinetic energy of beta particle will be 11.88 MeV, assuming that neutrinos have zero energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The decay constant of radioactive substance is 4.33 x 10-4 per year. Calculate its half life period.
(a) Write the basic nuclear process involved in the emission of β+ in a symbolic form, by a radioactive nucleus.
(b) In the reactions given below:
(i)`""_16^11C->_y^zB+x+v`
(ii)`""_6^12C+_6^12C->_a^20 Ne + _b^c He`
Find the values of x, y, and z and a, b and c.
Derive the mathematical expression for law of radioactive decay for a sample of a radioactive nucleus
Write symbolically the process expressing the β+ decay of `""_11^22Na`. Also write the basic nuclear process underlying this decay.
The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive `""_6^14"C"` present with the stable carbon isotope `""_6^12"C"`. When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of `""_6^14"C"` and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of `""_6^14"C"` dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjodaro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation.
The half-life of `""_38^90 "Sr"` is 28 years. What is the disintegration rate of 15 mg of this isotope?
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence
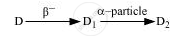
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is (i) the mass number (ii) atomic number of D?
The masses of 11C and 11B are respectively 11.0114 u and 11.0093 u. Find the maximum energy a positron can have in the β*-decay of 11C to 11B.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
28Th emits an alpha particle to reduce to 224Ra. Calculate the kinetic energy of the alpha particle emitted in the following decay:
`""^228"Th" → ""^224"Ra"^(∗) + alpha`
`""^224"Ra"^(∗) → ""^224"Ra" + γ (217 "keV")`.
Atomic mass of 228Th is 228.028726 u, that of 224Ra is 224.020196 u and that of `""_2^4H` is 4.00260 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the production of the radioactive isotope starts at t = 0. Find the number of active nuclei at time t.
The half-life of 40K is 1.30 × 109 y. A sample of 1.00 g of pure KCI gives 160 counts s−1. Calculate the relative abundance of 40K (fraction of 40K present) in natural potassium.
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
Consider a radioactive nucleus A which decays to a stable nucleus C through the following sequence:
A→B→C
Here B is an intermediate nuclei which is also radioactive. Considering that there are N0 atoms of A initially, plot the graph showing the variation of number of atoms of A and B versus time.
The activity R of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
| t (h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| R (MBq) | 100 | 35.36 | 12.51 | 4.42 | 1.56 |
- Plot the graph of R versus t and calculate the half-life from the graph.
- Plot the graph of ln `(R/R_0)` versus t and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
