Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
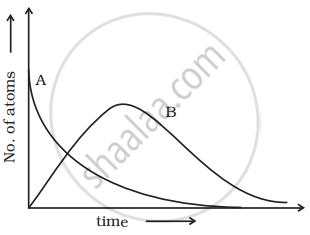
Consider a radioactive nucleus A which decays to a stable nucleus C through the following sequence:
A→B→C
Here B is an intermediate nuclei which is also radioactive. Considering that there are N0 atoms of A initially, plot the graph showing the variation of number of atoms of A and B versus time.
उत्तर
Consider radioactive nucleus A have N0 atoms of A initially; or at t = 0, NA = N0 (maximum) whole NB = 0. As time increases, NA decreases exponentially and the number of atoms of B increases. After some time NB becomes maximum. As B is an intermediate nuclei which is also radioactive, it also starts decaying and finally drops to zero exponentially by radioactive decay law. We can represent the situation as shown in the graph.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
Define the activity of a given radioactive substance. Write its S.I. unit.
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
57Co decays to 57Fe by β+- emission. The resulting 57Fe is in its excited state and comes to the ground state by emitting γ-rays. The half-life of β+- decay is 270 days and that of the γ-emissions is 10−8 s. A sample of 57Co gives 5.0 × 109 gamma rays per second. How much time will elapse before the emission rate of gamma rays drops to 2.5 × 109per second?
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
