Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The variation of decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in figure.
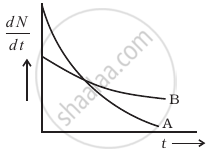
Which of the following statements are true?
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A.
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B but it does not always decay faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is smaller than that of A but still its decay rate becomes equal to that of A at a later instant.
पर्याय
a and b
a and c
b and d
c and d
उत्तर
c and d
Explanation:
It can be observed from the figure that the slope of curve A is greater than that of curve B, it means the rate of decay is faster for A than that of B.

According to Rutherford and Soddy's law for radioactive decay `-((dN)/(dt)) ∝ λ`, where decay. Hence at point P, the rate of decay for both A and B is the same.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
Define the term 'decay constant' of a radioactive sample. The rate of disintegration of a given radioactive nucleus is 10000 disintegrations/s and 5,000 disintegrations/s after 20 hr. and 30 hr. respectively from start. Calculate the half-life and the initial number of nuclei at t= 0.
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
The radioactivity of an old sample of whisky due to tritium (half-life 12.5 years) was found to be only about 4% of that measured in a recently purchased bottle marked 10 years old. The age of a sample is ______ years.
What is the half-life period of a radioactive material if its activity drops to 1/16th of its initial value of 30 years?
