Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
विकल्प
a and c
a and d
b and d
a and b
उत्तर
b and d
Explanation:
Law of radioactive disintegration: According to Rutherford and Soddy law for radioactive decay is as follows:
At any instant, the rate of decay of radioactive atoms is proportional to the number of atoms present at that instant.” i.e.
dN/dt ∞ N ⇒ dN/dt = – λN
it can be proved that N = N0e–λ1
In terms of mass M – M0e–λ1
where N = Number of atoms that remain undecayed after time t,
N0 = Number of atoms present initially (i.e., at t = 0),
M = Mass of radioactive nuclei at time t,
M0 = Mass ofradioactive nuclei at time t = 0,
N0 – N= Number of the disintegrated nuclei in time t,
dN/dt= rate of decay, λ = Decay constant or disintegration constant or radioactivity constant or Rutherford Soddy’s constant or the probability of decay per unit time of a nucleus.
The samples of the two radioactive nuclides A and B can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time if the initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
Also, when the initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive the mathematical expression for law of radioactive decay for a sample of a radioactive nucleus
Obtain the amount of `""_27^60"Co"` necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8.0 mCi strength. The half-life of `""_27^60"Co"` is 5.3 years.
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence
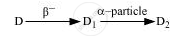
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is (i) the mass number (ii) atomic number of D?
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
A source contains two species of phosphorous nuclei, \[\ce{_15^32P}\] (T1/2 = 14.3 d) and \[\ce{_15^33P}\] (T1/2 = 25.3 d). At time t = 0, 90% of the decays are from \[\ce{_15^32P}\]. How much time has to elapse for only 15% of the decays to be from \[\ce{_15^32P}\]?
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?