Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following is a wrong description of binding energy of a nucleus?
पर्याय
It is the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent nucleons.
It is the energy made available when free nucleons combine to form a nucleus.
It is the sum of the rest mass energies of its nucleons minus the rest mass energy of the nucleus.
It is the sum of the kinetic energy of all the nucleons in the nucleus.
उत्तर
It is the sum of the kinetic energies of all the nucleons present in the nucleus.
Binding energy of a nucleus is defined as the energy required to break the nucleus into its constituents. It is also measured as the Q-value of the breaking of nucleus, i.e. the difference between the rest energies of reactants (nucleus) and the products (nucleons) or the difference between the kinetic energies of the products and the reactants.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Asha's mother read an article in the newspaper about a disaster that took place at Chernobyl. She could not understand much from the articles and asked a few questions from Asha regarding the article. Asha tried to answer her mother's questions based on what she learnt in Class XII Physics.
(a) What was the installation at Chernobyl where the disaster took place? What according to you, was the cause of this disaster?
(b) Explain the process of release of energy in the installation at Chernobyl.
(c) What according to you, were the values displayed by Asha and her mother?
Draw the plot of binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) as a functino of mass number A. Write two important conclusions that can be drawn regarding the nature of nuclear force.
Write the relationship between the size of a nucleus and its mass number (A)?
Using the curve for the binding energy per nucleon as a function of mass number A, state clearly how the release in energy in the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion can be explained.
A heavy nucleus X of mass number 240 and binding energy per nucleon 7.6 MeV is split into two fragments Y and Z of mass numbers 110 and 130. The binding energy of nucleons in Y and Z is 8.5 MeV per nucleon. Calculate the energy Q released per fission in MeV.
The mass number of a nucleus is equal to
As the mass number A increases, the binding energy per nucleon in a nucleus
In one average-life,
A neutron star has a density equal to that of the nuclear matter. Assuming the star to be spherical, find the radius of a neutron star whose mass is 4.0 × 1030 kg (twice the mass of the sun).
Calculate the mass of an α-particle. Its Its binding energy is 28.2 MeV.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
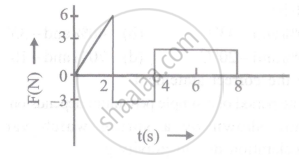
The force 'F' acting on a particle of mass 'm' is indicated by the force-time graph shown below. The change in momentum of the particle over the time interval from zero to 8s is:
A nucleus of mass M emits a γ-ray photon of frequency 'v'. The loss of internal energy by the nucleus is ______.
