Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why are alloys used for making standard resistance coils?
उत्तर
Alloys are used for making standard resistance coil because they have low-temperature coefficient of resistance with less temperature sensitivity.

This keeps the resistance of the wire almost constant even in small temperature change. The alloys also have high resistivity and hence high resistance, because for given length and cross-section area of conductor (L and A are constant). R α p
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
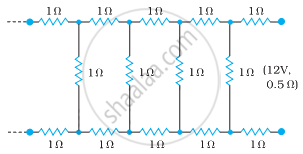
Determine the current drawn from a 12 V supply with internal resistance 0.5 Ω by the infinite network shown in the figure. Each resistor has 1 Ω resistance.
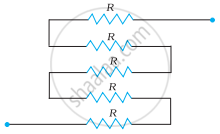
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
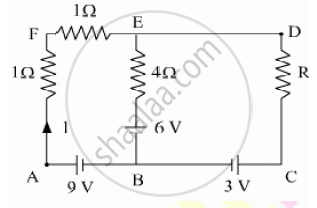
Using Kirchhoff’s rules determine the value of unknown resistance R in the circuit so that no current flows through 4 Ω resistance. Also find the potential difference between A and D.
Consider the following two statements:-
(A) Kirchhoff's junction law follows from conservation of charge.
(B) Kirchhoff's loop law follows from conservative nature of electric field.
Solve the following question.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, calculate the current through the 40 Ω and 20 Ω resistors in the following circuit.

State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
Lightning is a very good example of a natural current. In typical lightning, there is 109 J energy transfer across the potential difference of 5 × 107 V during a time interval of 0.2 s. Using this information, estimate the following quantities:
- the total amount of charge transferred between cloud and ground
- the current in the lightning bolt
- the power delivered in 0.2 s.

In a meter bridge the point D is a neutral point (Figure).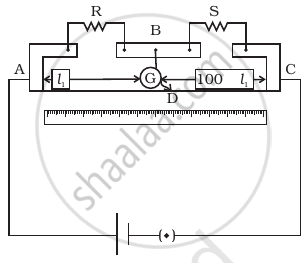
- The meter bridge can have no other neutral point for this set of resistances.
- When the jockey contacts a point on meter wire left of D, current flows to B from the wire.
- When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to the right of D, current flows from B to the wire through galvanometer.
- When R is increased, the neutral point shifts to left.
The circuit in figure shows two cells connected in opposition to each other. Cell E1 is of emf 6V and internal resistance 2Ω; the cell E2 is of emf 4V and internal resistance 8Ω. Find the potential difference between the points A and B.
