Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
उत्तर
(b) conservation of charge
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
Determine the current in each branch of the network shown in figure.

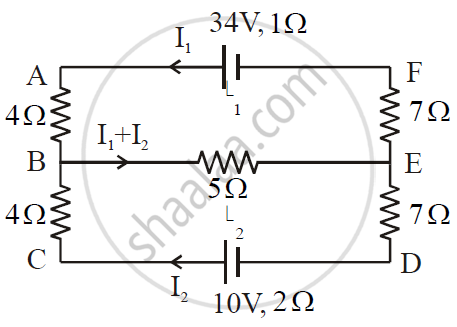
ε1 and ε2 are two batteries having emf of 34V and 10V respectively and internal resistance of 1Ω and 2Ω respectively. They are connected as shown in the figure below. Using Kirchhoff’s Laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of 6 Ω?
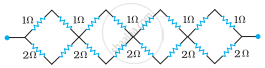
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
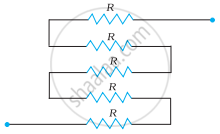
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules determine the value of unknown resistance R in the circuit so that no current flows through 4 Ω resistance. Also find the potential difference between A and D.
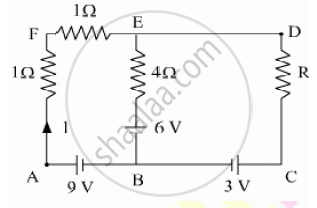
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

Consider the circuit shown in the figure. Find (a) the current in the circuit (b) the potential drop across the 5 Ω resistor (c) the potential drop across the 10 Ω resistor (d) Answer the parts (a), (b) and (c) with reference to the figure.
Twelve wires, each of equal resistance r, are joined to form a cube, as shown in the figure. Find the equivalent resistance between the diagonally-opposite points a and f.

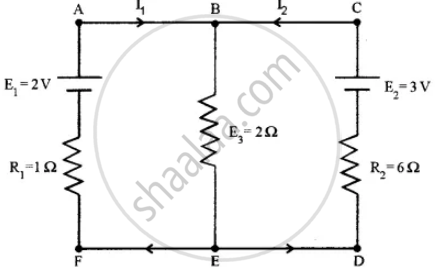
In the circuit shown in the figure below, E1 and E2 are two cells having emfs 2 V and 3 V respectively, and negligible internal resistance. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, find the values of currents l1 and I2.
Solve the following question.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, calculate the current through the 40 Ω and 20 Ω resistors in the following circuit.

State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
Obtain the condition for bridge balance in Wheatstone’s bridge.
How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
Lightning is a very good example of a natural current. In typical lightning, there is 109 J energy transfer across the potential difference of 5 × 107 V during a time interval of 0.2 s. Using this information, estimate the following quantities:
- the total amount of charge transferred between cloud and ground
- the current in the lightning bolt
- the power delivered in 0.2 s.

A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and resistance of 20 Ω. It is connected in series with resistance of 2980 Ω and a cell of emf 4 V. Calculate the potential along the wire.
Kirchhoff’s second law is a consequence of law of conservation of ______.
The e.m.f of The battery in a thermocouple is doubled. The rate of heat generated at one of the junction will.
What is the advantage of using thick metallic strips to join wires in a potentiometer?
Why are alloys used for making standard resistance coils?
Power P is to be delivered to a device via transmission cables having resistance RC. If V is the voltage across R and I the current through it, find the power wasted and how can it be reduced.
A 6-volt battery is connected to the terminals of a three-metre-long wire of uniform thickness and resistance of 100 ohms. The difference of potential between two points on the wire separated by a distance of 50 cm will be ______.
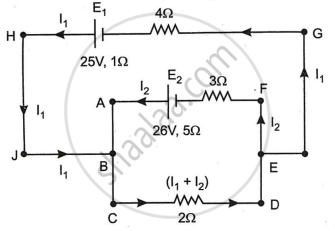
In the circuit shown in Figure below, E1 and E2 are batteries having emfs of 25V and 26V. They have an internal resistance of 1 Ω and 5 Ω respectively. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, calculate the currents I1 and I2.