Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Give reason:
Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
Sodium metal is stored under kerosene oil, Why?
उत्तर १
Sodium is highly reactive and reacts with both air and water. When exposed to air, it quickly combines with oxygen to form its oxide. Similarly, it reacts with water or moisture to produce sodium hydroxide.
\[\ce{4Na_{(s)} + O2_{(g)} -> 3Na2O_{(s)}}\]
\[\ce{2Na_{(s)}\underset{or moisture}{+ 2H2O_{(l)}} -> 2NaOH_{(aq)} + H2_{(g)}}\]
To protect sodium metal, it is typically stored under kerosene to prevent contact with air or moisture.
उत्तर २
- Sodium, potassium, and lithium are very reactive metals that react vigorously with air and water. Therefore, they are kept immersed in kerosene oil to prevent their contact with air and moisture.
- Sodium metal is highly reactive. Moisture in the air forms sodium hydroxide and releases hydrogen, which releases a significant amount of heat, resulting in fire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
.................... liberated when acetic acid reacts with sodium metal.
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Chlorine
(c) Oxygen
(d) Nitrogen
Metal A has electronic configuration (2, 8, 1) and metal B has (2, 8, 8, 2). Which is more reactive? Why? Identify these metals.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows.
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Cooper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the Table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
- Which is the most reactive metal?
- What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
- Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
The solution of Aluminium sulphate in water is .....................
(a) Green
(b) Colourless
(c) Pink
(d) Blue
Name the metal which has been placed at the top of the reactivity series.
What will happen if a strip of zinc is immersed in a solution of copper sulphate?
Complete and balance the following equation:
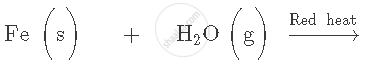
Name two metals which cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Give one example, with equation, of the displacement of hydrogen by a metal from an acid.
An element X reacts with hydrogen, when heated, to form a covalent hydride H2X. If H2X has a smell of rotten eggs, the element X is likely to be:
(a) carbon
(b) sulphur
(c) chlorine
(d) phosphorus
Which one of the following four metals would be displaced from the solution of its salt by the other three metals?
(a) Zn
(b) Ag
(c) Cu
(d) Mg
An element is soft and can be cut with a knife. If is very reactive and cannot be kept open in the air. It reacts vigorously with water. The element is most likely to be:
(a) Mg
(b) S
(c) P
(d) Na
An element X forms two oxides XO and XO2. The oxide XO has no action on litmus solution but oxide XO2 turns litmus solution red.
(a) What is the nature of oxide XO?
(b) What is the nature of oxide XO2?
(c) Would you call element X a metal or a non-metal? Give reason for your choice.
(d) Can you give an example of element like X?
In a solution of lead acetate, a strip of metal M was dipped. After some time, lead from the solution was deposited on the metal strip. Which metal is more reactive, M or lead?
Name a metal which It does not react with any physical state of water?
Write a chemical equation to illustrate the use of aluminium for joining cracked railway lines.
Rewrite the following statement by selecting the correct option.
A solution of Al2(SO4)3 in water is _____________.
Generally metals react with acids to give salt and hydrogen gas. Which of the following acids does not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg)?
An alkali metal A gives a compound B (molecular mass = 40) on reacting with water. The compound B gives a soluble compound C on treatment with aluminium oxide. Identify A, B and C and give the reaction involved.
