Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium, the quantity transmitted is ______.
पर्याय
matter.
energy.
energy and matter.
energy, matter and momentum.
उत्तर
With propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium, the quantity transmitted is energy.
Explanation:
A wave is a disturbance which propagates energy and momentum from one place to the other without the transport of matter. The propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium leads to the transmission of energy through the medium without the matter being transmitted. There is no movement of matter (mass) and hence momentum.
Important point:
Characteristics of wave motion:
- It is a sort of disturbance which travels through a medium.
- Material medium is essential for the propagation of mechanical waves.
- When a wave motion passes through a medium, particles of the medium only vibrate simply harmonically about their mean position. They do leave their position and move with the disturbance.
- There is a continuous phase difference amongst successive particles of the medium, i.e. particle 2 starts vibrating slightly later than particle 1 and so on.
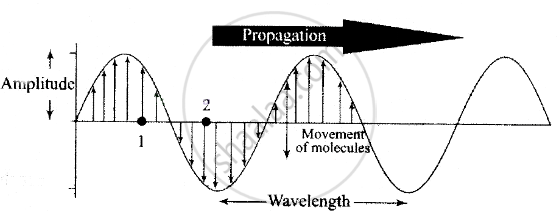
- The velocity of the particle during their vibration is different at different positions.
- The velocity of wave motion through a particular medium is constant. It depends only on die nature of the medium not on the frequency, wavelength or intensity,
- Energy is, propagated along with the wave motion without any net transport of the medium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
When you speak to your friend, which of the following parameters have a unique value in the sound produced?
A man stands before a large wall at a distance of 50.0 m and claps his hands at regular intervals. Initially, the interval is large. He gradually reduces the interval and fixes it at a value when the echo of a clap merges every 3 seconds, find the velocity of sound in air.
Find the minimum and maximum wavelengths of sound in water that is in the audible range (20−20000 Hz) for an average human ear. Speed of sound in water = 1450 m s−1.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
Calculate the bulk modulus of air from the following data about a sound wave of wavelength 35 cm travelling in air. The pressure at a point varies between (1.0 × 105 ± 14) Pa and the particles of the air vibrate in simple harmonic motion of amplitude 5.5 × 10−6 m.
A sources of sound operates at 2.0 kHz, 20 W emitting sound uniformly in all directions. The speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the density of air is 1.2 kg m −3. (a) What is the intensity at a distance of 6.0 m from the source? (b) What will be the pressure amplitude at this point? (c) What will be the displacement amplitude at this point?
If the sound level in a room is increased from 50 dB to 60 dB, by what factor is the pressure amplitude increased?
The two sources of sound, S1 and S2, emitting waves of equal wavelength 20.0 cm, are placed with a separation of 20.0 cm between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to S1 S2 and at a distance of 20.0 cm from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
A source of sound emitting a 1200 Hz note travels along a straight line at a speed of 170 m s−1. A detector is placed at a distance 200 m from the line of motion of the source. (a) Find the frequency of sound receive by the detector at the instant when the source gets closest to it. (b) Find the distance between the source and the detector at the instant in detects the frequency 1200 Hz. Velocity of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
