Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The two sources of sound, S1 and S2, emitting waves of equal wavelength 20.0 cm, are placed with a separation of 20.0 cm between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to S1 S2 and at a distance of 20.0 cm from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
उत्तर
Given:
Wavelength of sound wave λ = 20 cm
Separation between the two sources AC = 20cm
Distance of detector from source BD = 20 cm
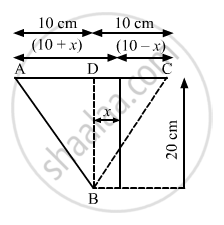
If the detector is moved through a distance x, then the path difference of the sound waves from sources A and C reaching B is given by:
Path difference = AB\[-\]BC
=\[\sqrt{\left( 20 \right)^2 + \left( 10 + x \right)^2} - \sqrt{\left( 20 \right)^2 + \left( 10 - x \right)^2}\]
To hear the minimum, this path difference should be equal to :
\[\frac{\left( 2n + 1 \right)\lambda}{2}\]=\[\frac{\lambda}{2}\]= 10 cm
So,
\[\sqrt{\left( 20 \right)^2 + \left( 10 + x \right)^2} - \sqrt{\left( 20 \right)^2 + \left( 10 - x \right)^2}\]= 10
On solving, we get, x = 12.6 cm.
Hence, the detector should be shifted by a distance of 12.6 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the smallest positive phase constant which is equivalent to 7⋅5 π?
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
A small source of sounds moves on a circle as shown in figure and an observer is sitting at O. Let \[v_1, v_2, v_3\] be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
Ultrasonic waves of frequency 4.5 MHz are used to detect tumour in soft tissue. The speed of sound in tissue is 1.5 km s−1 and that in air is 340 m s−1. Find the wavelength of this ultrasonic wave in air and in tissue.
A sources of sound operates at 2.0 kHz, 20 W emitting sound uniformly in all directions. The speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the density of air is 1.2 kg m −3. (a) What is the intensity at a distance of 6.0 m from the source? (b) What will be the pressure amplitude at this point? (c) What will be the displacement amplitude at this point?
If the sound level in a room is increased from 50 dB to 60 dB, by what factor is the pressure amplitude increased?
A string of length L fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at a frequency ν and a maximum amplitude A. (a)
- Find the wavelength and the wave number k.
- Take the origin at one end of the string and the X-axis along the string. Take the Y-axis along the direction of the displacement. Take t = 0 at the instant when the middle point of the string passes through its mean position and is going towards the positive y-direction. Write the equation describing the standing wave.
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
Two electric trains run at the same speed of 72 km h−1 along the same track and in the same direction with separation of 2.4 km between them. The two trains simultaneously sound brief whistles. A person is situated at a perpendicular distance of 500 m from the track and is equidistant from the two trains at the instant of the whistling. If both the whistles were at 500 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequencies heard by the person.
A small source of sound oscillates in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 17 cm. A detector is placed along the line of motion of the source. The source emits a sound of frequency 800 Hz which travels at a speed of 340 m s−1. If the width of the frequency band detected by the detector is 8 Hz, find the time period of the source.
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
A car moves with a speed of 54 km h−1 towards a cliff. The horn of the car emits sound of frequency 400 Hz at a speed of 335 m s−1. (a) Find the wavelength of the sound emitted by the horn in front of the car. (b) Find the wavelength of the wave reflected from the cliff. (c) What frequency does a person sitting in the car hear for the reflected sound wave? (d) How many beats does he hear in 10 seconds between the sound coming directly from the horn and that coming after the reflection?
A transverse wave is represented by y = 2sin (ωt - kx) cm. The value of wavelength (in cm) for which the wave velocity becomes equal to the maximum particle velocity, will be ______.
