Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
उत्तर
Yes, at the centre. The centre position is a node. If the string vibrates in its first overtone, then there will be two positions, i.e., two nodes, one at x = 0 and the other at x = L.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
A person can hear sound waves in the frequency range 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Find the minimum and the maximum wavelengths of sound that is audible to the person. The speed of sound is 360 m s−1.
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
The noise level in a classroom in absence of the teacher is 50 dB when 50 students are present. Assuming that on the average each student output same sound energy per second, what will be the noise level if the number of students is increased to 100?
Three sources of sound S1, S2 and S3 of equal intensity are placed in a straight line with S1S2 = S2S3. At a point P, far away from the sources, the wave coming from S2 is 120° ahead in phase of that from S1. Also, the wave coming from S3 is 120° ahead of that from S2. What would be the resultant intensity of sound at P?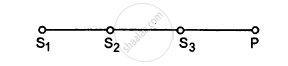
Two coherent narrow slits emitting sound of wavelength λ in the same phase are placed parallel to each other at a small separation of 2λ. The sound is detected by moving a detector on the screen ∑ at a distance D(>>λ) from the slit S1 as shown in figure. Find the distance x such that the intensity at P is equal to the intensity at O.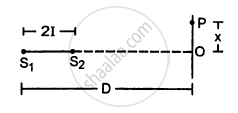
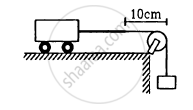
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
Show that if the room temperature changes by a small amount from T to T + ∆T, the fundamental frequency of an organ pipe changes from v to v + ∆v, where \[\frac{∆ v}{v} = \frac{1}{2}\frac{∆ T}{T} .\]
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
Two electric trains run at the same speed of 72 km h−1 along the same track and in the same direction with separation of 2.4 km between them. The two trains simultaneously sound brief whistles. A person is situated at a perpendicular distance of 500 m from the track and is equidistant from the two trains at the instant of the whistling. If both the whistles were at 500 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequencies heard by the person.
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
With propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium, the quantity transmitted is ______.
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
In the wave equation
`y = 0.5sin (2pi)/lambda(400t - x)m`
the velocity of the wave will be ______.
A transverse wave is represented by y = 2sin (ωt - kx) cm. The value of wavelength (in cm) for which the wave velocity becomes equal to the maximum particle velocity, will be ______.
