Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
उत्तर
The frequency of sound produced by vibration of vocal chords is amplified by resonance in the voice box. Now resonant frequency is directly proportional to the velocity of sound present in the voice box. Now as Helium has less density than air, velocity of sound in Helium is higher than that in air. Higher velocity of sound in Helium implies that the resonant frequency of the sound in voice chamber filled with Helium will be higher than with air. Thus the voice is high pitched in Helium filled voice box.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
The equation \[y = A \sin^2 \left( kx - \omega t \right)\]
represents a wave motion with
When sound wave is refracted from air to water, which of the following will remain unchanged?
When you speak to your friend, which of the following parameters have a unique value in the sound produced?
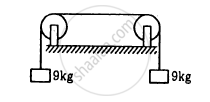
The length of the wire shown in figure between the pulley is 1⋅5 m and its mass is 12⋅0 g. Find the frequency of vibration with which the wire vibrates in two loops leaving the middle point of the wire between the pulleys at rest.
The intensity of sound from a point source is 1.0 × 10−8 W m−2 at a distance of 5.0 m from the source. What will be the intensity at a distance of 25 m from the source?
If the intensity of sound is doubled, by how many decibels does the sound level increase?
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
A string, fixed at both ends, vibrates in a resonant mode with a separation of 2⋅0 cm between the consecutive nodes. For the next higher resonant frequency, this separation is reduced to 1⋅6 cm. Find the length of the string.
A string of length L fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at a frequency ν and a maximum amplitude A. (a)
- Find the wavelength and the wave number k.
- Take the origin at one end of the string and the X-axis along the string. Take the Y-axis along the direction of the displacement. Take t = 0 at the instant when the middle point of the string passes through its mean position and is going towards the positive y-direction. Write the equation describing the standing wave.
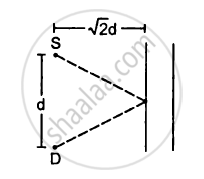
A source S and a detector D are placed at a distance d apart. A big cardboard is placed at a distance \[\sqrt{2}d\] from the source and the detector as shown in figure. The source emits a wave of wavelength = d/2 which is received by the detector after reflection from the cardboard. It is found to be in phase with the direct wave received from the source. By what minimum distance should the cardboard be shifted away so that the reflected wave becomes out of phase with the direct wave?
The two sources of sound, S1 and S2, emitting waves of equal wavelength 20.0 cm, are placed with a separation of 20.0 cm between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to S1 S2 and at a distance of 20.0 cm from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
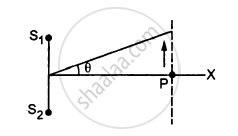
Two speakers S1 and S2, driven by the same amplifier, are placed at y = 1.0 m and y = −1.0 m(See figure). The speakers vibrate in phase at 600 Hz. A man stands at a point on the X-axis at a very large distance from the origin and starts moving parallel to the Y-axis. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1. (a) At what angle θ will the intensity of sound drop to a minimum for the first time? (b) At what angle will he hear a maximum of sound intensity for the first time? (c) If he continues to walk along the line, how many more can he hear?
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
The separation between a node and the next antinode in a vibrating air column is 25 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequency of vibration of the air column.
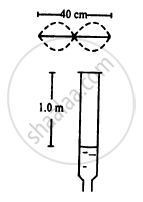
Consider the situation shown in the figure.The wire which has a mass of 4.00 g oscillates in its second harmonic and sets the air column in the tube into vibrations in its fundamental mode. Assuming that the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the tension in the wire.
A tuning fork produces 4 beats per second with another tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The first one is now loaded with a little wax and the beat frequency is found to increase to 6 per second. What was the original frequency of the tuning fork?
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
Equation of a plane progressive wave is given by `y = 0.6 sin 2π (t - x/2)`. On reflection from a denser medium its amplitude becomes 2/3 of the amplitude of the incident wave. The equation of the reflected wave is ______.
