Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When sound wave is refracted from air to water, which of the following will remain unchanged?
पर्याय
Wave number
Wavelength
Wave velocity
Frequency
उत्तर
Frequency
When a sound or light wave undergoes refraction, its frequency remains constant because there is no change in its phase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
At what temperature will the speed of sound be double of its value at 0°C?
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
The noise level in a classroom in absence of the teacher is 50 dB when 50 students are present. Assuming that on the average each student output same sound energy per second, what will be the noise level if the number of students is increased to 100?
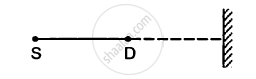
A source of sound S and detector D are placed at some distance from one another. a big cardboard is placed near hte detector and perpendicular to the line SD as shown in figure. It is gradually moved away and it is found that the intensity changes from a maximum to a minimum as the board is moved through a distance of 20 cm. Find the frequency of the sound emitted. Velocity of sound in air is 336 m s−1.
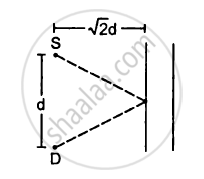
A source S and a detector D are placed at a distance d apart. A big cardboard is placed at a distance \[\sqrt{2}d\] from the source and the detector as shown in figure. The source emits a wave of wavelength = d/2 which is received by the detector after reflection from the cardboard. It is found to be in phase with the direct wave received from the source. By what minimum distance should the cardboard be shifted away so that the reflected wave becomes out of phase with the direct wave?
Two coherent narrow slits emitting sound of wavelength λ in the same phase are placed parallel to each other at a small separation of 2λ. The sound is detected by moving a detector on the screen ∑ at a distance D(>>λ) from the slit S1 as shown in figure. Find the distance x such that the intensity at P is equal to the intensity at O.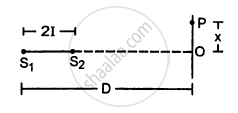
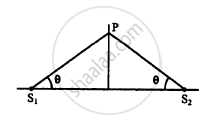
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
A tuning fork produces 4 beats per second with another tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The first one is now loaded with a little wax and the beat frequency is found to increase to 6 per second. What was the original frequency of the tuning fork?
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
A tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats per second with a wire of length 25 cm vibrating in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the length is slightly shortened. What could be the minimum length by which the wire we shortened so that it produces no beats with the tuning fork?
A boy riding on his bike is going towards east at a speed of 4√2 m s−1. At a certain point he produces a sound pulse of frequency 1650 Hz that travels in air at a speed of 334 m s−1. A second boy stands on the ground 45° south of east from his. Find the frequency of the pulse as received by the second boy.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
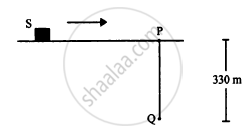
Figure shows a source of sound moving along X-axis at a speed of 22 m s−1continuously emitting a sound of frequency 2.0 kHz which travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener Q stands on the Y-axis at a distance of 330 m from the origin. At t = 0, the sources crosses the origin P. (a) When does the sound emitted from the source at P reach the listener Q? (b) What will be the frequency heard by the listener at this instant? (c) Where will the source be at this instant?
Which of the following statements are true for wave motion?
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
