Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
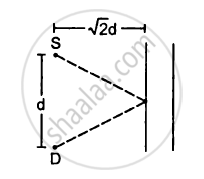
A source S and a detector D are placed at a distance d apart. A big cardboard is placed at a distance \[\sqrt{2}d\] from the source and the detector as shown in figure. The source emits a wave of wavelength = d/2 which is received by the detector after reflection from the cardboard. It is found to be in phase with the direct wave received from the source. By what minimum distance should the cardboard be shifted away so that the reflected wave becomes out of phase with the direct wave?
उत्तर
Given:
Distance between the source and detector = d
Distance of cardboard from the source =\[\sqrt{2d}\]
Wavelength of the source \[\lambda\]= d/2
Path difference between sound waves received by the detector before shifting the cardboard:
\[2\left( \sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \sqrt{2}d \right)^2} \right) - d\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2 \times \frac{3d}{2} - d\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2d\]
If the cardboard is shifted by a distance x, the path difference will be :
\[2\left( \sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \sqrt{2d} + x \right)^2} \right) - d\]
According to the question,
\[2\sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \sqrt{2}d + x \right)^2} - d = 2d + \frac{d}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \sqrt{2}d + x \right)^2} - d = \frac{9d}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\sqrt{\left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \sqrt{2}d + x \right)^2} = \frac{9d}{4} + d = \frac{13d}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( \frac{d}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \sqrt{2}d + x \right)^2 = \frac{169}{64} d^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( \sqrt{2}d + x \right)^2 = \frac{(169 - 16)}{64} d^2 = \frac{153}{64} d^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt{2}d + x = 1 . 54d\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \left( 1 . 54 - 1 . 41 \right)d = 0 . 13d\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If you are walking on the moon, can you hear the sound of stones cracking behind you? Can you hear the sound of your own footsteps?
Two loudspeakers are arranged facing each other at some distance. Will a person standing behind one of the loudspeakers clearly hear the sound of the other loudspeaker or the clarity will be seriously damaged because of the 'collision' of the two sounds in between?
A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
When you speak to your friend, which of the following parameters have a unique value in the sound produced?
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
A man stands before a large wall at a distance of 50.0 m and claps his hands at regular intervals. Initially, the interval is large. He gradually reduces the interval and fixes it at a value when the echo of a clap merges every 3 seconds, find the velocity of sound in air.
Ultrasonic waves of frequency 4.5 MHz are used to detect tumour in soft tissue. The speed of sound in tissue is 1.5 km s−1 and that in air is 340 m s−1. Find the wavelength of this ultrasonic wave in air and in tissue.
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
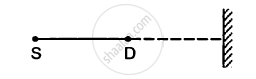
A source of sound S and detector D are placed at some distance from one another. a big cardboard is placed near hte detector and perpendicular to the line SD as shown in figure. It is gradually moved away and it is found that the intensity changes from a maximum to a minimum as the board is moved through a distance of 20 cm. Find the frequency of the sound emitted. Velocity of sound in air is 336 m s−1.
The two sources of sound, S1 and S2, emitting waves of equal wavelength 20.0 cm, are placed with a separation of 20.0 cm between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to S1 S2 and at a distance of 20.0 cm from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
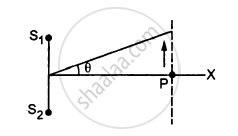
Two speakers S1 and S2, driven by the same amplifier, are placed at y = 1.0 m and y = −1.0 m(See figure). The speakers vibrate in phase at 600 Hz. A man stands at a point on the X-axis at a very large distance from the origin and starts moving parallel to the Y-axis. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1. (a) At what angle θ will the intensity of sound drop to a minimum for the first time? (b) At what angle will he hear a maximum of sound intensity for the first time? (c) If he continues to walk along the line, how many more can he hear?
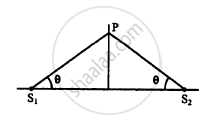
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A small speaker delivers 2W of audio output. At what distance from the speaker will one detect 120 dB intensity sound?
[Given reference intensity of sound as 10-12W/m2]
