Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
उत्तर
Given:
Velocity of sound in air v = 330 m/s
Velocity of sound through the steel tube vs = 5200 m/s
Here, Length of the steel tube S = 1 m
As we know,
\[t = \frac{S}{v}\]
\[t_1 = \frac{1}{330}\] and \[t_2 = \frac{1}{5200}\]
Where, t1 is the time taken by the sound in air.
t2 is the time taken by the sound in steel tube.
Therefore,
\[\text { Required time gap } t = t_1 - t_2\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = \left( \frac{1}{330} - \frac{1}{5200} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = 2 . 75 \times {10}^{- 3} s\]
\[ \Rightarrow t = 2 . 75 \text { ms }\]
Hence, the time gap between two hearings is 2.75 ms.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain what is Doppler effect in sound
A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
The equation of a travelling sound wave is y = 6.0 sin (600 t − 1.8 x) where y is measured in 10−5 m, t in second and x in metre. (a) Find the ratio of the displacement amplitude of the particles to the wavelength of the wave. (b) Find the ratio of the velocity amplitude of the particles to the wave speed.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
The absolute temperature of air in a region linearly increases from T1 to T2 in a space of width d. Find the time taken by a sound wave to go through the region in terms of T1, T2, d and the speed v of sound at 273 K. Evaluate this time for T1 = 280 K, T2 = 310 K, d = 33 m and v = 330 m s−1.
If the sound level in a room is increased from 50 dB to 60 dB, by what factor is the pressure amplitude increased?
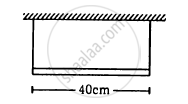
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
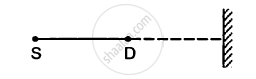
A source of sound S and detector D are placed at some distance from one another. a big cardboard is placed near hte detector and perpendicular to the line SD as shown in figure. It is gradually moved away and it is found that the intensity changes from a maximum to a minimum as the board is moved through a distance of 20 cm. Find the frequency of the sound emitted. Velocity of sound in air is 336 m s−1.
Two speakers S1 and S2, driven by the same amplifier, are placed at y = 1.0 m and y = −1.0 m(See figure). The speakers vibrate in phase at 600 Hz. A man stands at a point on the X-axis at a very large distance from the origin and starts moving parallel to the Y-axis. The speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1. (a) At what angle θ will the intensity of sound drop to a minimum for the first time? (b) At what angle will he hear a maximum of sound intensity for the first time? (c) If he continues to walk along the line, how many more can he hear?
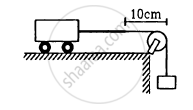
A heavy string is tied at one end to a movable support and to a light thread at the other end as shown in following figure. The thread goes over a fixed pulley and supports a weight to produce a tension. The lowest frequency with which the heavy string resonates is 120 Hz. If the movable support is pushed to the right by 10 cm so that the joint is placed on the pulley, what will be the minimum frequency at which the heavy string can resonate?
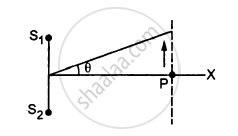
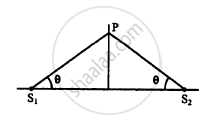
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
A tuning fork produces 4 beats per second with another tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The first one is now loaded with a little wax and the beat frequency is found to increase to 6 per second. What was the original frequency of the tuning fork?
A boy riding on a bicycle going at 12 km h−1 towards a vertical wall whistles at his dog on the ground. If the frequency of the whistle is 1600 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 330 m s−1, find (a) the frequency of the whistle as received by the wall (b) the frequency of the reflected whistle as received by the boy.
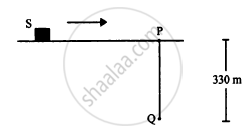
Figure shows a source of sound moving along X-axis at a speed of 22 m s−1continuously emitting a sound of frequency 2.0 kHz which travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener Q stands on the Y-axis at a distance of 330 m from the origin. At t = 0, the sources crosses the origin P. (a) When does the sound emitted from the source at P reach the listener Q? (b) What will be the frequency heard by the listener at this instant? (c) Where will the source be at this instant?
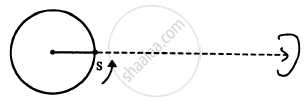
A small source of sound S of frequency 500 Hz is attached to the end of a light string and is whirled in a vertical circle of radius 1.6 m. The string just remains tight when the source is at the highest point. (a) An observer is located in the same vertical plane at a large distance and at the same height as the centre of the circle. The speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1 and g = 10 m s−2. Find the maximum frequency heard by the observer. (b) An observer is situated at a large distance vertically above the centre of the circle. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the sound emitted by the source when it is at the same height as the centre.
For the propagation of longitudinal waves, the medium must have
- elasticity
- mass
- inertia
- force of cohesion
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
A transverse wave is represented by y = 2sin (ωt - kx) cm. The value of wavelength (in cm) for which the wave velocity becomes equal to the maximum particle velocity, will be ______.
