Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the sound level in a room is increased from 50 dB to 60 dB, by what factor is the pressure amplitude increased?
उत्तर
Given:
Initial sound level \[\beta_1\] = 50 dB
Final sound level
\[\beta_2\]= 60 dB
Constant reference intensity \[I_0\]=\[10^{-12}\]W/m2
We can find initial intensity I1 using:
\[\beta_1 = 10 \log_{10} \left( \frac{I_1}{I_0} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 50 = 10 \log_{10} \left( \frac{I_1}{{10}^{- 12}} \right)\]
On Solving , We get:
\[I_1 =10^{-7} \]W/m2.
Similarly,
\[\beta_2 = 10 \log_{10} \left( \frac{I_2}{I_0} \right)\]
On substituting the values and solving, we get:
we have:
\[\frac{I_2}{I_1} = \left( \frac{p_2}{p_1} \right)^2 = \left( \frac{{10}^{- 6}}{{10}^{- 7}} \right) = 10\]
\[\therefore \left( \frac{p_2}{p_1} \right)^2 = 10\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{p_2}{p_1} = \sqrt{10}\]
Hence, the pressure amplitude is increased by
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The wavelengths of two sound waves in air are `81/173`m and `81/170`m. They produce 10 beats per second. Calculate the velocity of sound in air
When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
A person can hear sound waves in the frequency range 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Find the minimum and the maximum wavelengths of sound that is audible to the person. The speed of sound is 360 m s−1.
Find the minimum and maximum wavelengths of sound in water that is in the audible range (20−20000 Hz) for an average human ear. Speed of sound in water = 1450 m s−1.
Ultrasonic waves of frequency 4.5 MHz are used to detect tumour in soft tissue. The speed of sound in tissue is 1.5 km s−1 and that in air is 340 m s−1. Find the wavelength of this ultrasonic wave in air and in tissue.
The intensity of sound from a point source is 1.0 × 10−8 W m−2 at a distance of 5.0 m from the source. What will be the intensity at a distance of 25 m from the source?
A particular guitar wire is 30⋅0 cm long and vibrates at a frequency of 196 Hz when no finger is placed on it. The next higher notes on the scale are 220 Hz, 247 Hz, 262 Hz and 294 Hz. How far from the end of the string must the finger be placed to play these notes?
The two sources of sound, S1 and S2, emitting waves of equal wavelength 20.0 cm, are placed with a separation of 20.0 cm between them. A detector can be moved on a line parallel to S1 S2 and at a distance of 20.0 cm from it. Initially, the detector is equidistant from the two sources. Assuming that the waves emitted by the sources are in detector should be shifted to detect a minimum of sound.
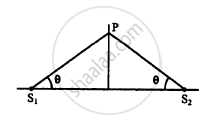
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
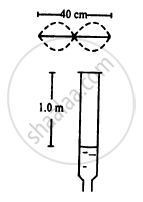
Consider the situation shown in the figure.The wire which has a mass of 4.00 g oscillates in its second harmonic and sets the air column in the tube into vibrations in its fundamental mode. Assuming that the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the tension in the wire.
A tuning fork produces 4 beats per second with another tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The first one is now loaded with a little wax and the beat frequency is found to increase to 6 per second. What was the original frequency of the tuning fork?
Show that if the room temperature changes by a small amount from T to T + ∆T, the fundamental frequency of an organ pipe changes from v to v + ∆v, where \[\frac{∆ v}{v} = \frac{1}{2}\frac{∆ T}{T} .\]
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
A source of sound emitting a 1200 Hz note travels along a straight line at a speed of 170 m s−1. A detector is placed at a distance 200 m from the line of motion of the source. (a) Find the frequency of sound receive by the detector at the instant when the source gets closest to it. (b) Find the distance between the source and the detector at the instant in detects the frequency 1200 Hz. Velocity of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
During propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave ______.
- all the particles are vibrating in the same phase.
- amplitude of all the particles is equal.
- particles of the medium executes S.H.M.
- wave velocity depends upon the nature of the medium.
