Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
उत्तर
Given:
The sound level that can hurt the human ear is 120 dB. Then, the intensity I is 1 W/m2.
Audio output of the small speaker P = 2 W
Let the closest distance be x.
We have:
\[I = \frac{P}{4\pi r^2}\]
\[\left( \frac{2}{4\pi x^2} \right) = 1\]
\[\Rightarrow x^2 = \left( \frac{2}{4\pi} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 0 . 4 m = 40 \text { cm }\]
Hence, the closest distance of the human ear from the small speaker is 40 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the smallest positive phase constant which is equivalent to 7⋅5 π?
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
The equation \[y = A \sin^2 \left( kx - \omega t \right)\]
represents a wave motion with
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
A tuning fork sends sound waves in air. If the temperature of the air increases, which of the following parameters will change?
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
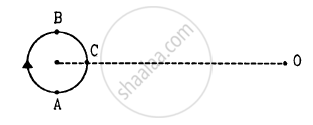
A small source of sounds moves on a circle as shown in figure and an observer is sitting at O. Let \[v_1, v_2, v_3\] be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.
When you speak to your friend, which of the following parameters have a unique value in the sound produced?
A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Velocity of sound
(c) Wavelength
(d) Time period
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
Find the minimum and maximum wavelengths of sound in water that is in the audible range (20−20000 Hz) for an average human ear. Speed of sound in water = 1450 m s−1.
Sound waves from a loudspeaker spread nearly uniformly in all directions if the wavelength of the sound is much larger than the diameter of the loudspeaker. (a)Calculate the frequency for which the wavelength of sound in air is ten times the diameter of the speaker if the diameter is 20 cm. (b) Sound is essentially transmitted in the forward direction if the wavelength is much shorter than the diameter of the speaker. Calculate the frequency at which the wavelength of the sound is one tenth of the diameter of the speaker described above. Take the speed of sound to be 340 m/s.
Ultrasonic waves of frequency 4.5 MHz are used to detect tumour in soft tissue. The speed of sound in tissue is 1.5 km s−1 and that in air is 340 m s−1. Find the wavelength of this ultrasonic wave in air and in tissue.
The absolute temperature of air in a region linearly increases from T1 to T2 in a space of width d. Find the time taken by a sound wave to go through the region in terms of T1, T2, d and the speed v of sound at 273 K. Evaluate this time for T1 = 280 K, T2 = 310 K, d = 33 m and v = 330 m s−1.
Calculate the bulk modulus of air from the following data about a sound wave of wavelength 35 cm travelling in air. The pressure at a point varies between (1.0 × 105 ± 14) Pa and the particles of the air vibrate in simple harmonic motion of amplitude 5.5 × 10−6 m.
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
The fundamental frequency of a closed pipe is 293 Hz when the air in it is a temperature of 20°C. What will be its fundamental frequency when the temperature changes to 22°C?
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
In an experiment to determine the velocity of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube, the first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm for a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The velocity of the sound at room temperature is 336 ms-1. The third resonance is observed when the air column has a length of ______ cm.
