Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A source of sound S and detector D are placed at some distance from one another. a big cardboard is placed near hte detector and perpendicular to the line SD as shown in figure. It is gradually moved away and it is found that the intensity changes from a maximum to a minimum as the board is moved through a distance of 20 cm. Find the frequency of the sound emitted. Velocity of sound in air is 336 m s−1.
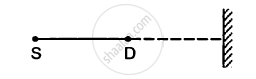
उत्तर
Given:
Velocity of sound in air v = 336 ms−1
Distance between maximum and minimum intensity :
\[\frac{\lambda}{4}\]= 20 cm
Frequency of sound f = ?
We have :
\[\frac{\lambda}{4} = 20\]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = 20 \times 4 = 80 \text { cm } = 80 \times {10}^{- 2} \text { m }\]
As we know ,
\[v = f\lambda\]
\[\therefore\] \[f = \frac{v}{\lambda}\]
\[\Rightarrow f = \frac{336}{80 \times {10}^{- 2}} = 420 \text { Hz }\]
Therefore, the frequency of the sound emitted from the source is 420 Hz.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The equation \[y = A \sin^2 \left( kx - \omega t \right)\]
represents a wave motion with
The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
When sound wave is refracted from air to water, which of the following will remain unchanged?
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
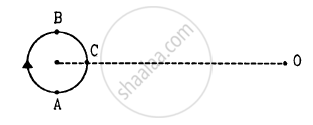
A small source of sounds moves on a circle as shown in figure and an observer is sitting at O. Let \[v_1, v_2, v_3\] be the frequencies heard when the source is at A, B and C respectively.
An electrically maintained tuning fork vibrates with constant frequency and constant amplitude. If the temperature of the surrounding air increases but pressure remains constant, the produced will have
(a) larger wavelength
(b) larger frequency
(c) larger velocity
(d) larger time period.
A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Velocity of sound
(c) Wavelength
(d) Time period
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
A string of length L fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at a frequency ν and a maximum amplitude A. (a)
- Find the wavelength and the wave number k.
- Take the origin at one end of the string and the X-axis along the string. Take the Y-axis along the direction of the displacement. Take t = 0 at the instant when the middle point of the string passes through its mean position and is going towards the positive y-direction. Write the equation describing the standing wave.
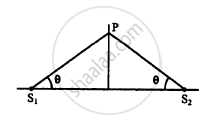
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
In a standing wave pattern in a vibrating air column, nodes are formed at a distance of 4.0 cm. If the speed of sound in air is 328 m s−1, what is the frequency of the source?
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
Two electric trains run at the same speed of 72 km h−1 along the same track and in the same direction with separation of 2.4 km between them. The two trains simultaneously sound brief whistles. A person is situated at a perpendicular distance of 500 m from the track and is equidistant from the two trains at the instant of the whistling. If both the whistles were at 500 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequencies heard by the person.
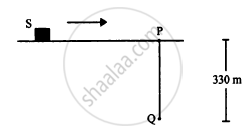
Figure shows a source of sound moving along X-axis at a speed of 22 m s−1continuously emitting a sound of frequency 2.0 kHz which travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener Q stands on the Y-axis at a distance of 330 m from the origin. At t = 0, the sources crosses the origin P. (a) When does the sound emitted from the source at P reach the listener Q? (b) What will be the frequency heard by the listener at this instant? (c) Where will the source be at this instant?
For the propagation of longitudinal waves, the medium must have
- elasticity
- mass
- inertia
- force of cohesion
Equation of a plane progressive wave is given by `y = 0.6 sin 2π (t - x/2)`. On reflection from a denser medium its amplitude becomes 2/3 of the amplitude of the incident wave. The equation of the reflected wave is ______.
A small speaker delivers 2W of audio output. At what distance from the speaker will one detect 120 dB intensity sound?
[Given reference intensity of sound as 10-12W/m2]
