Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two electric trains run at the same speed of 72 km h−1 along the same track and in the same direction with separation of 2.4 km between them. The two trains simultaneously sound brief whistles. A person is situated at a perpendicular distance of 500 m from the track and is equidistant from the two trains at the instant of the whistling. If both the whistles were at 500 Hz and the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1, find the frequencies heard by the person.
उत्तर
Given:
Speed of sound in air v = 340 ms−1
Frequency of whistles \[f_0\]= 500 Hz
Speed of train \[v_s\]= 72 km/h =\[72 \times \frac{5}{18} = 20 \text { m/s }\]
The person will receive the sound in a direction that makes an angle θ with the track. The angle θ is given by :
\[\theta = \tan^{- 1} \left( \frac{0 . 5}{2 . 4/2} \right) = 22 . 62^\circ\]
The velocity of the source will be 'v cos θ' when heard by the observer.
So, the apparent frequency received by the man from train A is
\[f_1 = \left( \frac{v}{v - v_s \cos\theta} \right) \times f_0 \]
\[ \Rightarrow f_1 = \left( \frac{340}{340 - v_s \cos 22 . {62}^\circ} \right) \times 500\]
\[ \Rightarrow f_1 = \left( \frac{340}{340 - 20 \times \cos 22 . 62^\circ} \right) \times 500\]
\[ \Rightarrow f_1 = 528 . 70 \text{ Hz } \approx 529 \text { Hz }\]
The apparent frequency heard by the man from train B is
\[f_2 = \left( \frac{v}{v + v\cos\theta} \right) \times f_0 \]
\[ \Rightarrow f_2 = \left( \frac{340}{340 + 20 \times \cos 22 . 62^\circ} \right) \times 500\]
\[ \Rightarrow f_2 = 474 . 24 \text { Hz } \approx 474 \text { Hz }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain what is Doppler effect in sound
The voice of a person, who has inhaled helium, has a remarkably high pitch. Explain on the basis of resonant vibration of vocal cord filled with air and with helium.
When we clap our hands, the sound produced is best described by Here p denotes the change in pressure from the equilibrium value.
Two sound waves move in the same direction in the same medium. The pressure amplitudes of the waves are equal but the wavelength of the first wave is double the second. Let the average power transmitted across a cross section by the first wave be P1 and that by the second wave be P2. Then
A listener is at rest with respect to the source of sound. A wind starts blowing along the line joining the source and the observer. Which of the following quantities do not change?
(a) Frequency
(b) Velocity of sound
(c) Wavelength
(d) Time period
A steel tube of length 1.00 m is struck at one end. A person with his ear closed to the other end hears the sound of the blow twice, one travelling through the body of the tube and the other through the air in the tube. Find the time gap between the two hearings. Use the table in the text for speeds of sound in various substances.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
The sound level at a point 5.0 m away from a point source is 40 dB. What will be the level at a point 50 m away from the source?
A uniform horizontal rod of length 40 cm and mass 1⋅2 kg is supported by two identical wires as shown in figure. Where should a mass of 4⋅8 kg be placed on the rod so that the same tuning fork may excite the wire on left into its fundamental vibrations and that on right into its first overtone? Take g = 10 m s−2.
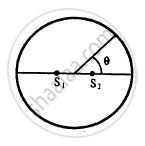
Figure shown two coherent sources S1 and S2 which emit sound of wavelength λ in phase. The separation between the sources is 3λ. A circular wire of large radius is placed in such way that S1,S2 is at the centre of the wire. Find the angular positions θ on the wire for which constructive interference takes place.
A tuning fork produces 4 beats per second with another tuning fork of frequency 256 Hz. The first one is now loaded with a little wax and the beat frequency is found to increase to 6 per second. What was the original frequency of the tuning fork?
Show that if the room temperature changes by a small amount from T to T + ∆T, the fundamental frequency of an organ pipe changes from v to v + ∆v, where \[\frac{∆ v}{v} = \frac{1}{2}\frac{∆ T}{T} .\]
A piano wire A vibrates at a fundamental frequency of 600 Hz. A second identical wire Bproduces 6 beats per second with it when the tension in A is slightly increased. Find the the ratio of the tension in A to the tension in B.
A boy riding on his bike is going towards east at a speed of 4√2 m s−1. At a certain point he produces a sound pulse of frequency 1650 Hz that travels in air at a speed of 334 m s−1. A second boy stands on the ground 45° south of east from his. Find the frequency of the pulse as received by the second boy.
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A person standing on a road sends a sound signal to the driver of a car going away from him at a speed of 72 km h−1. The signal travelling at 330 m s−1 in air and having a frequency of 1600 Hz gets reflected from the body of the car and returns. Find the frequency of the reflected signal as heard by the person.
A source of sound emitting a 1200 Hz note travels along a straight line at a speed of 170 m s−1. A detector is placed at a distance 200 m from the line of motion of the source. (a) Find the frequency of sound receive by the detector at the instant when the source gets closest to it. (b) Find the distance between the source and the detector at the instant in detects the frequency 1200 Hz. Velocity of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
For the propagation of longitudinal waves, the medium must have
- elasticity
- mass
- inertia
- force of cohesion
A small speaker delivers 2W of audio output. At what distance from the speaker will one detect 120 dB intensity sound?
[Given reference intensity of sound as 10-12W/m2]
