Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Equation of a plane progressive wave is given by `y = 0.6 sin 2π (t - x/2)`. On reflection from a denser medium its amplitude becomes 2/3 of the amplitude of the incident wave. The equation of the reflected wave is ______.
पर्याय
`y = 0.6 sin 2π (t + x/2)`
`y = - 0.4 sin 2π (t + x/2)`
`y = 0.4 sin 2π (t + x/2)`
`y = - 0.4 sin 2π (t - x/2)`
उत्तर
Equation of a plane progressive wave is given by `y = 0.6 sin 2π (t - x/2)`. On reflection from a denser medium its amplitude becomes 2/3 of the amplitude of the incident wave. The equation of the reflected wave is `underline(y = - 0.4 sin 2π (t + x/2))`.
Explanation:
The amplitude of a reflected wave `A_r = 2/3 xx A_i = 2/3 xx 0.6` = 0.4 units
Given the equation of incident wave `y_i = 0.6 sin 2π (t - x/2)`
The Equation of reflected wave is `y_i = A_r sin 2π (t + x/2 + π)` ......[∵ At denser medium, phase changes by π]
The positive sign is due to the reversal of direction of the proportion
So, `y_r = - 0.4 sin 2π (t + x/2)` ......[∵ sin(π + θ) = – sinθ]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
A string clamped at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode. Is there any position (except the ends) on the string which can be touched without disturbing the motion? What if the string vibrates in its first overtone?
Two tuning forks vibrate with the same amplitude but the frequency of the first is double the frequency of the second. Which fork produces more intense sound in air?
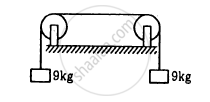
The length of the wire shown in figure between the pulley is 1⋅5 m and its mass is 12⋅0 g. Find the frequency of vibration with which the wire vibrates in two loops leaving the middle point of the wire between the pulleys at rest.
The intensity of sound from a point source is 1.0 × 10−8 W m−2 at a distance of 5.0 m from the source. What will be the intensity at a distance of 25 m from the source?
If the intensity of sound is doubled, by how many decibels does the sound level increase?
A particular guitar wire is 30⋅0 cm long and vibrates at a frequency of 196 Hz when no finger is placed on it. The next higher notes on the scale are 220 Hz, 247 Hz, 262 Hz and 294 Hz. How far from the end of the string must the finger be placed to play these notes?
Two coherent narrow slits emitting sound of wavelength λ in the same phase are placed parallel to each other at a small separation of 2λ. The sound is detected by moving a detector on the screen ∑ at a distance D(>>λ) from the slit S1 as shown in figure. Find the distance x such that the intensity at P is equal to the intensity at O.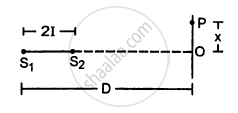
A small source of sound oscillates in simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 17 cm. A detector is placed along the line of motion of the source. The source emits a sound of frequency 800 Hz which travels at a speed of 340 m s−1. If the width of the frequency band detected by the detector is 8 Hz, find the time period of the source.
In an experiment to determine the velocity of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube, the first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm for a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The velocity of the sound at room temperature is 336 ms-1. The third resonance is observed when the air column has a length of ______ cm.
