Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The fundamental frequency of a vibrating organ pipe is 200 Hz.
(a) The first overtone is 400 Hz.
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
उत्तर
(b) The first overtone may be 400 Hz.
(c) The first overtone may be 600 Hz.
(d) 600 Hz is an overtone.
For an open organ pipe: \[\nu_n = n \nu_1\]
nth harmonic = (n – 1)th overtone
\[\nu_1 = 200 Hz, \nu_2 = 400 Hz, \nu_3 = 600 Hz\]
If the pipe is an open organ pipe, then the 1st overtone is 400 Hz. Option (b) is correct.
Also, υ3 = 600 Hz, i.e., second overtone = 600 Hz.
600 Hz is an overtone. Therefore, option (d) is correct.
If the pipe is a closed organ pipe, then
\[\nu_n = \left( 2n - 1 \right) \nu_1\]
(2n – 1)th harmonic = (n – 1)th overtone
For n = 2:
1st overtone = 3rd harmonic = 3υ1
=3 × 200
= 600 Hz
Therefore, option (c) is also correct.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wave is represented by an equation \[y = c_1 \sin \left( c_2 x + c_3 t \right)\] In which direction is the wave going? Assume that \[c_1 , c_2\] \[c_3\] are all positive.
The bulk modulus and the density of water are greater than those of air. With this much of information, we can say that velocity of sound in air
A tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz is vibrated with a sonometer wire and 6 beats per second are heard. The beat frequency reduces if the tension in the string is slightly increased. The original frequency of vibration of the string is
A person can hear sound waves in the frequency range 20 Hz to 20 kHz. Find the minimum and the maximum wavelengths of sound that is audible to the person. The speed of sound is 360 m s−1.
Two point sources of sound are kept at a separation of 10 cm. They vibrate in phase to produce waves of wavelength 5.0 cm. What would be the phase difference between the two waves arriving at a point 20 cm from one source (a) on the line joining the sources and (b) on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the sources?
Sound with intensity larger than 120 dB appears pain full to a person. A small speaker delivers 2.0 W of audio output. How close can the person get to the speaker without hurting his ears?
A string of length L fixed at both ends vibrates in its fundamental mode at a frequency ν and a maximum amplitude A. (a)
- Find the wavelength and the wave number k.
- Take the origin at one end of the string and the X-axis along the string. Take the Y-axis along the direction of the displacement. Take t = 0 at the instant when the middle point of the string passes through its mean position and is going towards the positive y-direction. Write the equation describing the standing wave.
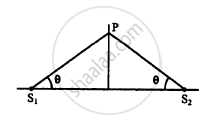
Two sources of sound S1 and S2 vibrate at same frequency and are in phase. The intensity of sound detected at a point P as shown in the figure is I0. (a) If θ equals 45°, what will be the intensity of sound detected at this point if one of the sources is switched off? (b) What will be the answer of the previous part if θ = 60°?
Show that if the room temperature changes by a small amount from T to T + ∆T, the fundamental frequency of an organ pipe changes from v to v + ∆v, where \[\frac{∆ v}{v} = \frac{1}{2}\frac{∆ T}{T} .\]
A traffic policeman standing on a road sounds a whistle emitting the main frequency of 2.00 kHz. What could be the apparent frequency heard by a scooter-driver approaching the policeman at a speed of 36.0 km h−1? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A sound source, fixed at the origin, is continuously emitting sound at a frequency of 660 Hz. The sound travels in air at a speed of 330 m s−1. A listener is moving along the lien x= 336 m at a constant speed of 26 m s−1. Find the frequency of the sound as observed by the listener when he is (a) at y = − 140 m, (b) at y = 0 and (c) at y = 140 m.
A train running at 108 km h−1 towards east whistles at a dominant frequency of 500 Hz. Speed of sound in air is 340 m/s. What frequency will a passenger sitting near the open window hear? (b) What frequency will a person standing near the track hear whom the train has just passed? (c) A wind starts blowing towards east at a speed of 36 km h−1. Calculate the frequencies heard by the passenger in the train and by the person standing near the track.
During propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave ______.
- all the particles are vibrating in the same phase.
- amplitude of all the particles is equal.
- particles of the medium executes S.H.M.
- wave velocity depends upon the nature of the medium.
In an experiment to determine the velocity of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube, the first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm for a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The velocity of the sound at room temperature is 336 ms-1. The third resonance is observed when the air column has a length of ______ cm.
The speed of a wave in a string is 20 m/s and the frequency is 50 Hz. The phase difference between two points on the string 10 cm apart will be ______.
In the wave equation
`y = 0.5sin (2pi)/lambda(400t - x)m`
the velocity of the wave will be ______.
A small speaker delivers 2W of audio output. At what distance from the speaker will one detect 120 dB intensity sound?
[Given reference intensity of sound as 10-12W/m2]
