Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2023-2024
Date & Time: 27th February 2024, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
Read the following instructions carefully and follow them:
- This question paper contains 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections - Section A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A - question number 1 to 16 are multiple choice type questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Section B - question number 17 to 21 are very short answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks.
- Section C - question number 22 to 28 are short answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks.
- Section D - question number 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question carries 4 marks.
- Section E - question number 31 to 33 are long answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice given in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions in all the Sections except section A.
- Kindly note that there is a separate question paper for Visually Impaired candidates.
- Use of calculator is NOT allowed.
The specific sequence in which amino acids are arranged in a protein is called its ______.
Primary structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
Quaternary structure
Chapter:
The correct name of the given reaction is:
\[\ce{Ar - N+2X- ->[Cu CN/KCN] Ar - CN + N2}\]
Sandmeyer’s reaction
Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis
Carbyl amine reaction
Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction
Chapter:
Out of the following alkenes, the one which will produce tertiary butyl alcohol on acid catalysed hydration is:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH = CH2}\]
\[\ce{CH3CH = CH2}\]
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - CH3}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)2C = CH2}\]
Chapter:
Auto-oxidation of chloroform in air and sunlight produces a poisonous gas known as ______.
Tear gas
Mustard gas
Phosgene gas
Chlorine gas
Phosphine
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Transition metals are known to make interstitial compounds. Formation of interstitial compounds makes the transition metal ______.
more hard
more soft
more ductile
more metallic
Chapter:
Isotonic solutions have the same ______.
density
refractive index
osmotic pressure
volume
Chapter:
Which of the following cell was used in the Apollo space programme?
Mercury cell
Daniel cell
\[\ce{H2 - O2}\] fuel cell
Dry cell
\[\ce{Ni - Cd}\] cell
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
The rate of a reaction increases sixteen times when the concentration of the reactant increases four times. The order of the reaction is ______.
2.5
2.0
1.5
0.5
Chapter:
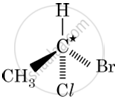
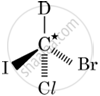
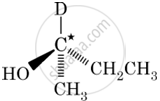
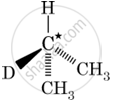
In which of the following molecules, C atom marked with asterisk is chiral?
I, II, III
I, II, III, IV
II, III, IV
I, III, IV
Chapter:
Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?
\[\ce{OH-}\]
\[\ce{C6H5O-}\]
\[\ce{RO-}\]
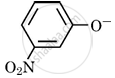
Chapter:
Dilution affects both conductivity as well as molar conductivity. Effect of dilution on both is as follows:
both increase with dilution.
both decrease with dilution.
conductivity increases whereas molar conductivity decreases on dilution.
conductivity decreases whereas molar conductivity increases on dilution.
Chapter:
Van't Hoff factor for \[\ce{Na2SO4*10H2O}\] solution, assuming complete ionization is ______.
1
3
13
2
Chapter:
Assertion (A): \[\ce{Zr}\] and \[\ce{Hf}\] are of almost similar atomic radii.
Reason (R): This is due to Lanthanoid contraction.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): The units of rate constant of a zero order reaction and rate of reaction are the same.
Reason (R): In zero order reaction, the rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of reactants.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Inversion of configuration is observed in SN2 reaction.
Reason (R): The reaction proceeds with the formation of carbocation.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): p-methoxyphenol is a stronger acid than p-nitrophenol.
Reason (R): Methoxy group shows +I effect whereas nitro group shows −I effect.
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Chapter:
State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
State Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Classify the following sugars into monosaccharides and disaccharides:
Galactose, Glucose, Lactose and Maltose
Chapter:
Carry out the following conversion:
Nitrobenzene to Aniline
Chapter:
How do you convert the following:
Aniline to phenol
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Advertisements
Write a chemical test to distinguish between Dimethyl amine and Ethanamine.
Chapter:
Write the product formed when benzene diazonium chloride is treated with KI.
Chapter:
Show that in case of a first order reaction, the time taken for completion of 99% reaction is twice the time required for 90% completion of the reaction. (log 10 = 1)
Chapter:
Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.2 mol L−1 \[\ce{KCl}\] solution is 200 Ω. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.05 mol L−1 \[\ce{KCl}\] solution is 620 Ω, calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.05 mol L−1 \[\ce{KCl}\] solution. The conductivity of 0.2 mol L−1 \[\ce{KCl}\] solution is 0.0248 S cm−1.
Chapter:
Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compound.
\[\ce{[Co(NH3)4Cl(NO2)]Cl}\]
Chapter:
Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compound:
\[\ce{[Ni(NH3)6]Cl2}\]
Chapter:
Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compound:
\[\ce{K3[Cr(C2O4)3]}\]
Chapter:
Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compound:
\[\ce{[Co(en)2Br2]+}\]
Chapter:
Give the structure of the major product expected from the following reaction:
Reaction of Ethanal with methyl-magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis.
Chapter:
Give the structure of the major product expected from the following reaction:
Hydration of But-1-ene in the presence of dilute sulphuric acid.
Chapter:
Give the structure of the major product expected from the following reaction:
Reaction of phenol with bromine water.
Chapter:
Draw the structure of major product in the following reaction:
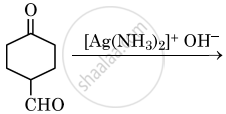
Chapter:
Draw the structure of major product in the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.......}\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}\\
\backslash\phantom{......}/\phantom{.......}\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C = C \phantom{.....}->[NaOI]}\\
/\phantom{......}\backslash\phantom{.......}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{........}\ce{C - CH3}\\
\phantom{...}||\\
\phantom{...}\ce{O}\\
\end{array}\]
Chapter:
Draw the structure of major product in the following reaction:
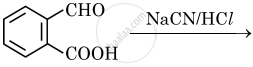
Chapter:
Calculate the emf of the following cell:
\[\ce{Ni_{(s)} + 2Ag+(0.01 M) -> Ni^{2+} (0.1 M) + 2Ag_{(s)}}\]
Given that `E_(cell)^0` = 1.05 V, log 10 = 1
Chapter:
Account for the following:
Haloalkanes react with \[\ce{AgCN}\] to form isocyanide as main product.
Chapter:
Account for the following:
Allyl chloride shows high reactivity towards SN1 reaction.
Chapter:
Account for the following:
Haloarenes are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Chapter:
The rate constant of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 300 K to 320 K. Calculate the activation energy for this reaction.
[log 2 = 0.30, log 4 = 0.60, 2.303 R = 19.15 JK−1mol−1]
Chapter:
A compound 'X’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C3H9N}\] reacts with \[\ce{C6H5SO2Cl}\] to give a solid, insoluble in alkali. Identify 'X’ and give the IUPAC name of the product. Write the reaction involved.
Chapter:
The following question is a case-based question. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| The oxidation number of the central atom in a complex is defined as the charge it would carry if all the ligands are removed along with the electron pairs that are shared with the central atom. Similarly, the charge on the complex is the sum of the charges of the constituent parts, i.e., the sum of the charges on the central metal ion and its surrounding ligands. Based on this, the complex is called neutral if the sum of the charges of the constituents is equal to zero. However, for an anion or cationic complex, the sum of the charges of the constituents is equal to the charge on the coordination sphere. |
Based on the above information, answer the following questions:
(a) Define ambidentate ligand with an example. (1)
(b) What type of isomerism is shown by \[\ce{[CO(NH3)5Cl]SO4}\] and \[\ce{[Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl}\]? (1)
(c) Define Chelate effect. How it affects the stability of complex? (2)
OR
(c) Find the coordination number and oxidation state of chromium in \[\ce{Na3[Cr(C2O4)3]}\]. (2)
Chapter:
Advertisements
The following question is a case-based question. Read the case carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Certain organic compounds are required in small amounts in our diet but their deficiency causes specific diseases. These compounds are called vitamins. Most of the vitamins cannot be synthesized in our body but plants can synthesize almost all of them. So they are considered as essential food factors. However, the bacteria of the gut can produce some of the vitamins required by us. All the vitamins are generally available in our diet. The term ‘vitamin’ was coined from the words vital + amine, since the earlier identified compounds had an amino group. Vitamins are classified into two groups depending upon their solubility in water or fat, namely, fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. |
Answer the following questions:
(a) What is the other name of vitamin B6? (1)
(b) Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes increased blood clotting time. (1)
(c) Xerophthalmia is caused by the deficiency of which vitamin? Give two sources of this vitamin. (2)
OR
(c) Why can’t vitamin C be stored in our body? Name the disease caused by the deficiency of this vitamin. (2)
Chapter:
\[\ce{Ce(III)}\] is easily oxidised to \[\ce{Ce(IV)}\]. Comment.
Chapter:
E°(Mn2+/Mn) is −1.18 V. Why is this value highly negative in comparison to neighbouring d block elements?
Chapter:
Which element of 3d series has lowest enthalpy of atomisation and why?
Chapter:
What happens when sodium chromate is acidified?
Chapter:
Give reasons for the following statement:
\[\ce{Zn}\], \[\ce{Cd}\] and \[\ce{Hg}\] are soft metals.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Why \[\ce{HCl}\] should not be used for potassium permanganate titrations?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
The lower oxides of transition metals are basic, whereas the highest are amphoteric/acidic. Give reason.
Chapter:
Ishan’s automobile radiator is filled with 1.0 kg of water. How many grams of ethylene glycol (Molar mass = 62 g mol−1) must Ishan add to get the freezing point of the solution lowered to −2.8°C. Kf for water is 1.86 K kg mol−1.
Chapter:
What type of deviation is shown by a mixture of ethanol and acetone? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Boiling point of water at 750 mm \[\ce{Hg}\] pressure is 99.68°C. How much sucrose (Molar mass = 342 g mol−1) is to be added to 500 g of water such that it boils at 100°C? (Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol−1).
Chapter:
An organic compound (A) with the molecular formula \[\ce{C9H10O}\] forms a 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Fehling solution and undergoes the Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzene dicarboxylic acid.
- Identify the compound (A) and write its IUPAC name. (2)
- Write the reaction of compound (A) with
- 2, 4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine and
- Fehling solution. (2)
- Write the equation of compound (A) when it undergoes the Cannizzaro reaction. (1)
Chapter:
Why is the α-hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Account for the following:
Oxidation of aldehydes is easier than ketones.
Chapter:
Arrange the following in decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions:
Propanal, Acetone, Benzaldehyde
Chapter:
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling point:
Propane, Ethanol, Dimethylether, Propanal
Chapter:
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Benzaldehyde and Benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2023 - 2024
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2024 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.