Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Being Alive - What is its Meaning?
3: The Cell - A Unit of Life
4: Tissues
5: Vegetative Propagation
6: Biotechnology Applications
7: Flowers
8: Pollination and Fertilization
9: Seeds: Structure and Germination
▶ 10: Respiration in Plants
11: Understanding EcoSystems
12: Interaction Between Biotic and Abiotic Factors in an EcoSystem
13: Diversity of Life and Classification
14: Bacteria and Fungi: Their Importance
15: Nutrition in Man
16: Digestive System
17: The Skeletal System
18: Structure and Function of Skin
19: Respiratory System
20: Health: Causes of Diseases
21: Health: Personal and Social
22: Sources of Waste
23: Safe Disposal of Wastes
![Frank solutions for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 10 - Respiration in Plants Frank solutions for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 10 - Respiration in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-9-icse_6:77732ab511d24be4a4c5dcfc00fdbe57.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Respiration in Plants
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CISCE Frank for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE 10 Respiration in Plants Exercise [Pages 87 - 90]
What do you understand by respiration?
What are the respiratory substrates? Give two examples.
Write the overall equation of aerobic respiration.
What is alcoholic fermentation?
Which process is common to aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Where does glycolysis take place in the living cell?
Name the cell organelle in which Kreb's take place.
Distinguish between:
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration.
Distinguish between:
Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
Differentiate between Respiration and Combustion.
How will you demonstrate that energy is released during aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Do you agree that respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis?
Match the terms of column A with the statements in column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Yeast | (a) partial breakdown of food substance. |
| (ii) Glucose | (b) nutrients are oxidized without using molecular oxygen by the process of fermentation. |
| (iii) Anaerobic | (c) is the best organic substrate for respiration. |
| (iv) Glycolysis | (d) the intermediate substance in the breakdown of glucose. |
| (v) Pyruvic acid | (e) the series of changes from glucose to pyruvic acid in respiration. |
Given alongside is an experimental set up to demonstrate a phenomenon in a plant:
(a) What is the aim of this experiment?
(b) Why was the bell jar covered with a black cloth?
(c) What is the function of caustic soda in this experiment?
(d) Give an overall chemical equation of the process mentioned in (a) above.
(e) Mention one precaution that should be taken to ensure more accurate results. What change, if any, would you observe in the lime water in Flask A and B? In each case give a reason for your answer.

Fill in the blank:
Fermentation is a type of ______ respiration.
Fill in the blank:
The first phase of respiration is ______.
Fill in the blank:
______ is the last product of glycolysis.
Fill in the blank:
The final hydrogen acceptor in aerobic respiration is ______.
Fill in the blank:
In living cells glycolysis occurs in ______.
Write True or False against the following statement:
Combustion is a biological process.
True
False
Write True or False against the following statement:
Kreb's cycle is common to both types of respiration.
True
False
Write True or False against the following statement:
Glycolysis takes place in the crystal of the mitochondria.
True
False
Write True or False against the following statement:
Protein is the first choice as a respiratory substrate.
True
False
Write True or False against the following statement:
The respiration is faster than combustion.
True
False
Moist germinated seeds were placed in a thermos flask A, and germinating seeds, which were boiled and then soaked in 5 percent formalin, were placed in thermos flask B. Thermometers were inserted in the flask and the mouth of each flask plugged with moist cotton wool. The two flasks were fixed upside down as shown in the fig. 10.9. The temperature on both thermometers was noted. After about 48 hours, the temperature in flask A was found to be much higher than that in flask B.
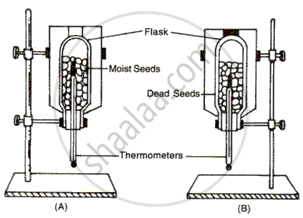
(a) State the object of using the apparatus.
(b) Explain, why a rise in temperature occurs in flask A.
(c) If 5 percent formalin was not used after boiling the seeds, the temperature of flask B would have risen considerably. Explain.
Complete the following statement by selecting the correct alternative from the ones given below:
The immediate source of energy for metabolic reactions in a living cell is ______.
glucose ATP
protein
Give the overall chemical equation that represents anaerobic respiration in plants.
Mention any three points in which respiration is exactly the opposite of photosynthesis.
The given fig. refers to an apparatus which is used to demonstrate a physiological process:
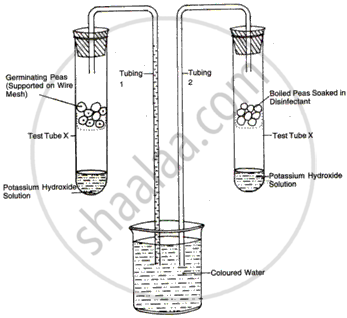
(a) What is the purpose of keeping potassium hydroxide solution in test tubes X and Y?
(b) What is the purpose of keeping boiled peas soaked in disinfectant in test tube Y?
(c) Why has coloured water risen in tube 1?
(d) Name the biological process which causes the above rise.
(e) Define the biological process shown in the experiment.
Write scientific term for the following:
The powerhouse of the cell.
Write scientific term for the following:
Anaerobic respiration in the muscles.
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative out of those given below.
Every living cell of the plant
respire
photosynthesizes
as well as photosynthesizes
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative out of those given below.
Normally, respiration takes place in
day
night
day and night
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative out of those given below.
Carbon dioxide and water are formed in
photosynthesis
aerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative out of those given below.
In respiration, temperature
rises
comes down
remains the same
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative out of those given below.
In respiration, energy is released in
controlled manner
uncontrolled manner
the form of light
Name the following:
The process of living beings which is concerned with the release of energy for use in the body.
Name the following:
The energy currency of the body.
Name the following:
The respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen.
Name the following:
The respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
Name the following:
The chemicals generally used to absorb carbon dioxide in respiratory experiments.
Name the following:
The solution that turns milky when carbon dioxide is passed through that solution.
Name the following:
The products formed as a result of aerobic respiration.
Name the following:
The products formed as a result of anaerobic respiration.
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
In the process of respiration
ADP is converted to ATP.
Glucose is converted to carbon dioxide.
Glucose is converted to carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy.
Pyruvic acid is converted to ATP.
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Which order is right for cellular respiration from the following
Electron transfer, glycolysis, Kreb's cycle.
Kreb's cycle, electron transfer, glycolysis.
Electron transfer, Kreb's cycle, glycolysis.
Glycolysis, Kreb's cycle, electron transfer.
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Less energy is liberated in anaerobic respiration in yeast in comparison with aerobic respiration because
Energy is not formed by oxygen.
Less CO2 is formed.
Energy is left in alcohol.
Yeast requires less energy.
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
The role of oxygen in cellular respiration
To form CO2
To liberate energy from hydrogen storage.
To change pyruvate into acetyl CoA.
To accept hydrogen and form water.
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
The materials formed in anaerobic respiration are
CO2 and water
CO2 and alcohol
CO2 and formaldehyde
CO2 and hemoglobin
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
The reactions of Kerb's cycle occurs in
Lysosomes
grana
Mitochondria
endoplasmic reticulum
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Who discovered the Kreb's cycle?
Kolliker
Hens Krebs
Altman
Benda
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Alcohol is produced during the process of
photosynthesis
aerobic respiration
combustion
fermentation
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
The energy liberated during respiration is stored in the form of
heat
ATP
ADP
NADP
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Mitochondria is the storage house for:
NADH
Pyruvic acid
ATP
Citric acid
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
How many ATP molecules are gained in glycolysis?
Zero
Two
Four
Eight
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
Where does glycolysis take place?
In cytoplasm
In chloroplast
In ribosome
In mitochondria
The question has four options. Choose the correct answer:
The energy liberated in aerobic respiration is
637 Kcal
600 Kcal
673 Kcal
693 Kcal
Solutions for 10: Respiration in Plants
![Frank solutions for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 10 - Respiration in Plants Frank solutions for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 10 - Respiration in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-9-icse_6:77732ab511d24be4a4c5dcfc00fdbe57.jpg)
Frank solutions for Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 10 - Respiration in Plants
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 10 (Respiration in Plants) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 10 Respiration in Plants are Respiration Vs. Burning (Combustion), Types of Respiration: Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration, Experiments on Respiration in Plants, Respiration and Photosynthesis, Organs of Respiratory Exchange, Respiration in Plant, Respiration, Phases of Respiration: Glycolysis, Phases of Respiration: Electron Transport System (Ets) and Oxidative Phosphorylation, Phases of Respiration: Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle Or Kreb’s Cycle), Phases of Respiration: Pyruvate Oxidation (Link Reaction), Phases of Respiration: Fermentation, Formation of ATP.
Using Frank Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Respiration in Plants exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Respiration in Plants Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
