Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Biological Classification
3: Plant Kingdom
4: Animal Kingdom
5: Morphology of Flowering Plants
6: Anatomy of Flowering Plants
7: Structural Organisation in Animals
8: Cell : the Unit of Life
9: Biomolecules
10: Cell Cycle and Cell Division
11: Transport in Plants
12: Mineral Nutrition
▶ 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
14: Respiration in Plants
15: Plant Growth and Development
16: Digestion and Absorption
17: Breathing and Exchange of Gases
18: Body Fluids and Circulation
19: Excretory Products and Their Elimination
20: Locomotion and Movement
21: Neural Control and Coordination
22: Chemical Coordination and Integration
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 13 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Biology [English] Class 11.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Exercises [Pages 68 - 76]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Which metal ion is a constituent of chlorophyll?
Iron
Copper
Magnesium
Zinc
Which pigment acts directly to convert light energy to chemical energy?
Chlorophyll a
Chlorophyll b
Xanthophyll
Carotenoid
Which range of wavelength (in nm) is called photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)?
100 – 390
390 – 430
400 – 700
760 – 100,00
Which light range is least effective in photosynthesis?
Blue
Green
Red
Violet
Chemosynthetic bacteria obtain energy from ______.
Sun
Infra red rays
Organic substances
Inorganic chemicals
Energy required for ATP synthesis in PSII comes from ______.
Proton gradient
Electron gradient
Reduction of glucose
Oxidation of glucose
During light reaction in photosynthesis the following are formed ______.
ATP and sugar
Hydrogen, O2 and sugar
ATP, hydrogen and O2
ATP, hydrogen and O2 donor
Dark reaction in photosynthesis is called so because ______.
It can occur in dark also
It does not depend on light energy
It cannot occur during day light
It occurs more rapidly at night
PEP is primary CO2 acceptor in ______.
C4 plants
C3 plants
C2 plants
Both C3 and C4 plants
Splitting of water is associated with ______.
Photosystem I
Lumen of thylakoid
Both Photosystem I and II
Inner surface of thylakoid membrane
The correct sequence of flow of electrons in the light reaction is ______.
PSII, plastoquinone, cytochromes, PSI, ferredoxin
PSI, plastoquinone, cytochromes, PSII, ferredoxin
PSI, ferredoxin, PSII
PSI, plastoquinone, cytochromes, PSII, ferredoxin
The enzyme that is not found in a C3 plant is ______.
RuBP Carboxylase
PEP Carboxylase
NADP reductase
ATP synthase
The reaction that is responsible for the primary fixation of CO2 is catalysed by ______.
RuBP carboxylase
PEP carboxylase
RuBP carboxylase and PEP carboxylase
PGA synthase
When CO2 is added to PEP, the first stable product synthesised is ______.
Pyruvate
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
Phosphoglycerate
Oxaloacetate
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Examine the figure
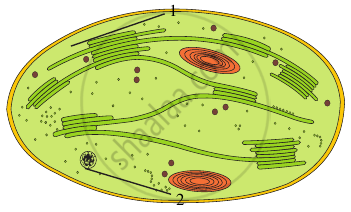
- Is this structure present in animal cell or plant cell?
- Can these be passed on to the progeny? How?
- Name the metabolic processes taking place in the places marked (1) and (2).
\[\ce{2H2O -> 4H^{+} + O2 + 4e^{-}}\]
Based on the above equation, answer the following questions:
- Where does this reaction take place in plants?
- What is the significance of this reaction?
Cyanobacteria and some other photosynthetic bacteria don’t have chloroplasts. How do they conduct photosynthesis?
NADP reductase enzyme is located on ______.
Breakdown of proton gradient leads to release of ______.
Can girdling experiments be done in monocots? If yes, How? If no, why not?
\[\ce{3CO2 + 9ATP + 6NADPH + Water -> glyceraldehyde 3 – phosphate + 9 ADP + 6 NADP+ + 8 Pi}\]
Analyze the above reaction and answer the following questions:
- How many molecules of ATP and NADPH are required to fix one molecule of CO2?
- Where in the chloroplast does this process occur?
Does moonlight support photosynthesis?
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the C4 cycle. Explain.
Hatch slack pathway
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the C4 cycle. Explain.
Calvin cycle
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the C4 cycle. Explain.
PEP carboxylase
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the C4 cycle. Explain.
Bundle sheath cells
Where is NADP reductase enzyme located in the chloroplast? What is the role of this enzyme in proton gradient development?
ATPase enzyme consists of two parts. What are those parts? How are hey arranged in the thylakoid membrane? Conformational change occur n which part of the enzyme?
Which products formed during the light reaction of photosynthesis are used to drive the dark reaction?
What is the basis for designating C3 and C4 pathways of photosynthesis?
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Succulents are known to keep their stomata closed during the day to check transpiration. How do they meet their photosynthetic CO2 requirements?
Chlorophyll ‘a’ is the primary pigment for light reaction. What are accessory pigments? What is their role in photosynthesis?
Do reactions of photosynthesis called, as ‘Dark Reaction’ need light? Explain.
How are photosynthesis and respiration related to each other?
If a green plant is kept in dark with proper ventilation, can this plant carry out photosynthesis? Can anything be given as supplement to maintain its growth or survival?
Photosynthetic organisms occur at different depths in the ocean. Do they receive qualitatively and quantitatively the same light? How do they adapt to carry out photosynthesis under these conditions?
In tropical rain forests, the canopy is thick and plants growing below receive filtered light. How are they able to carry out photosynthesis?
What conditions enable Rubirco to function as an oxygenase? Explain the ensuing process.
Why does the rate of photosynthesis decrease at higher temperatures?
Explain how during light reaction of photosynthesis, ATP synthesis is a chemiosmotic phenomenon.
Find out how Melvin Calvin worked out the complete biosynthetic pathway for synthesis of sugar.
Six turns of calvin cycle are required to generate one mole of glucose. Explain.
Complete the flow chart for cyclic photophosphorylation of the photosystem-I

In what kind of plants do you come across ‘Kranz’ anatomy? To which conditions are those plants better adapted? How are these plants better adapted than the plants which lack this anatomy?
In a way green plants and cyanobacteria have synthesized all the food on the earth. Comment.
Tomatoes, carrots and chillies are red in colour due to the presence of one pigment. Name the pigment. Is it a photosynthetic pigment?
Why do we believe chloroplast and mitochondria to be semi-autonomous organelle?
Observe the diagram and answer the following.

- Which group of plants exibits these two types of cells?
- What is the first product of C4 cycle?
- Which enzyme is there in bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells?
A cyclic process is occurring in C3 plant, which is light dependent, and needs O2. This process doesn’t produce energy rather it consumes energy.
- Can you name the given process?
- Is it essential for survival?
- What are the end products of this process?
- Where does it occur?
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Is it correct to say that photosynthesis occurs only in leaves of a plant? Besides leaves, what are the other parts that may be capable of carrying out photosynthesis? Justify.
The entire process of photosynthesis consists of a number of reactions. Where in the cell do these take place?
Synthesis of ATP and NADPH ______
The entire process of photosynthesis consists of a number of reactions. Where in the cell do these take place?
Photolysis of water ______
The entire process of photosynthesis consists of a number of reactions. Where in the cell do these take place?
Fixation of CO2 ______
The entire process of photosynthesis consists of a number of reactions. Where in the cell do these take place?
Synthesis of sugar molecule ______
The entire process of photosynthesis consists of a number of reactions. Where in the cell do these take place?
Synthesis of starch ______
Which property of the pigment is responsible for its ability to initiate the process of photosynthesis? Why is the rate of photosynthesis higher in the red and blue regions of the spectrum of light?
What can we conclude from the statement that the action and absorption spectrum of photosynthesis overlap? At which wavelength do they show peaks?
Under what conditions are C4 plants superior to C3?
In the figure given below, the black line (upper) indicates action spectrum for photosynthesis and the lighter line (lower) indicates the absorption spectrum of chlorophyll a. Answer the following:

- What does the action spectrum indicate? How can we plot an action spectrum?
- How can we derive an absorption spectrum for any substance?
List the important events and end products of the light reaction?
In the diagram given below what is label A, B and C. What type of phosphorylation is possible in this?

Why is the RuBisCo enzyme more appropriately called RUBP Carboxylase-Oxygenase and what important role does it play in photosynthesis?
What special anatomical features are displayed by leaves of C4 plants? How do they provide advantage over the structure of C3 plants?
Name the two important enzymes of C4 pathway, and explain their role in fixing CO2?
Why is RuBisCo enzyme the most abundant enzyme in the world?
Why photorespiration does not take place in C4 plants?
Solutions for 13: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-11_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE 13 (Photosynthesis in Higher Plants) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 11 chapter 13 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants are Early Experiments on Photosynthesis, Where Does Photosynthesis Take Place?, Pigments Are Involved in Photosynthesis, Light Dependent Reaction (Hill Reaction \ Light Reaction), Electron Transport, Electron Transport - Photolysis / Splitting of Water, Electron Transport - Cyclic and Non-cyclic Photo-phosphorylation, Electron Transport - Chemiosmotic Hypothesis, Primary Acceptor of CO2, The Calvin Cycle, The C4 Pathway, Photorespiration, Factors Affecting Photosynthesis, Photosynthesis as a Mean of Autotrophic Nutrition, Chloroplast Structure, Site of Photosynthesis, Light-independent Reactions, Photosynthesis Reaction, Photochemical and Biosynthetic Phases of Photosynthesis, Photosynthesis in Higher Plants (Questions).
Using NCERT Exemplar Biology [English] Class 11 solutions Photosynthesis in Higher Plants exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Biology [English] Class 11 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 13, Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Biology [English] Class 11 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 11 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
