Advertisements
Chapters
2: Is Matter Around Us Pure
3: Atoms and Molecules
4: Structure of the Atom
5: The Fundamental Unit of Life
6: Tissues
7: Diversity In Living Organisms
▶ 8: Motion
9: Force and Laws of Motion
10: Gravitation
11: Work and Energy
12: Sound
13: Why Do We Fall Ill
14: Natural Resources
15: Improvement In Food Resources
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Motion NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Motion
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Science [English] Class 9.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 8 Motion Multiple Choice Questions [Pages 57 - 58]
A particle is moving in a circular path of radius r. The displacement after half a circle would be:
Zero
πr
2r
2πr
A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity u, the greatest height h to which it will rise is,
`"u"/"g"`
`"u"^2/(2"g")`
`"u"^2/"g"`
`"u"/(2"g")`
The numerical ratio of displacement to distance for a moving object is :
always less than 1
equal to 1 or more than 1
always more than 1
equal to 1 or less than 1
If the displacement of an object is proportional to the square of time, then the object is moving with :
uniform velocity
uniform acceleration
increasing acceleration
decreasing acceleration
From the given v – t graph (Fig. 8.1), it can be inferred that the object is
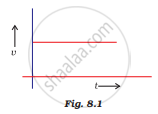
in uniform motion
at rest
in non-uniform motion
moving with uniform acceleration
Area under a v – t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit
m2
m
m3
m s–1
Four cars A, B, C, and D are moving on a levelled road. Their distance versus time graphs are shown in Fig. 8.2. Choose the correct statement.
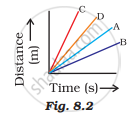
Car A is faster than car D.
Car B is the slowest.
Car D is faster than car C.
Car C is the slowest
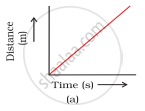
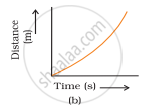
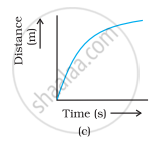
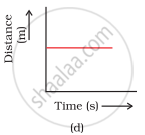
Which of the following figures (Fig. 8.3) represents uniform motion of a moving object correctly?
Slope of a velocity-time graph gives
the distance
the displacement
the acceleration
the speed
In which of the following cases of motions, the distance moved and the magnitude of displacement are equal?
If the car is moving on a straight road
If the car is moving in a circular path
The pendulum is moving to and fro
The earth is revolving around the Sun
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 8 Motion Short Answer Questions [Pages 59 - 60]
The displacement of a moving object in a given interval of time is zero. Would the distance travelled by the object also be zero? Justify your answer.
How will the equations of motion for an object moving with a uniform velocity change?
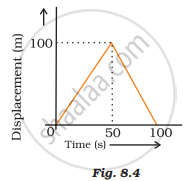
A girl walks along a straight path to drop a letter in the letterbox and comes back to her initial position. Her displacement–time graph is shown in Fig.8.4. Plot a velocity-time graph for the same.
A car starts from rest and moves along the x-axis with constant acceleration 5 ms–2 for 8 seconds. If it then continues with constant velocity, what distance will the car cover in 12 seconds since it started from the rest?
A motorcyclist drives from A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h–1 and returns back with a speed of 20 km h–1. Find its average speed.
The velocity-time graph (Fig. 8.5) shows the motion of a cyclist. Find (i) its acceleration (ii) its velocity and (iii) the distance covered by the cyclist in 15 seconds.

Draw a velocity versus time graph of a stone thrown vertically upwards and then coming downwards after attaining the maximum height.
An object is dropped from rest at a height of 150 m and simultaneously another object is dropped from rest at a height of 100 m. What is the difference in their heights after 2s if both the objects drop with the same accelerations? How does the difference in heights vary with time?
An object starting from rest travels 20 m in the first 2 s and 160 m in the next 4 s. What will be the velocity after 7 s from the start?
Using the following data, draw time - displacement graph for a moving object:
| Time (s) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
| Displacement (m) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
Use this graph to find average velocity for the first 4 s, for the next 4 s and for the last 6 s.
An electron moving with a velocity of 5 × 104 ms−1 enters into a uniform electric field and acquires a uniform acceleration of 104 ms–2 in the direction of its initial motion.
(i) Calculate the time in which the electron would acquire a velocity double of its initial velocity.
(ii) How much distance the electron would cover at this time?
Obtain a relation for the distance travelled by an object moving with uniform acceleration in the interval between 4th and 5th seconds.
Two stones are thrown vertically upwards simultaneously with their initial velocities u1 and u2 respectively. Prove that the heights reached by them would be in the ratio of `"u"_1^2 : "u"_2^2` (Assume upward acceleration is –g and downward acceleration to be +g)
Solutions for 8: Motion
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Motion NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 8 - Motion
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE 8 (Motion) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 9 chapter 8 Motion are Motion and Rest, Motion Along a Straight Line, Types of Motion, Measuring the Rate of Motion - Speed with Direction, Rate of Change of Velocity, Describing Motion, Distance and Displacement, Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph, Velocity - Time Graphs, Equations of Motion by Graphical Method, Derivation of Velocity - Time Relation by Graphical Method, Derivation of Displacement - Time Relation by Graphical Method, Derivation of Displacement - Velocity Relation by Graphical Method, Uniform Circular Motion (UCM), Motion (Numerical).
Using NCERT Exemplar Science [English] Class 9 solutions Motion exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Motion Science [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.