Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A body falls towards earth in air. Will its total mechanical energy be conserved during the fall? Justify.
Solution
The total mechanical energy of the free-falling body is not conserved as this energy is used against the force of friction from the air molecules.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A heavy stone is thrown from a cliff of height h with a speed v. The stoen will hit the ground with maximum speed if it is thrown
A heavy stone is thrown in from a cliff of height h in a given direction. The speed with which it hits the ground
(a) must depend on the speed of projection
(b) must be larger than the speed of projection
(c) must be independent of the speed of projection
(d) may be smaller than the speed of projection.
Figure shows a particle sliding on a frictionless track which terminates in a straight horizontal section. If the particle starts slipping from point A, how far away from the track will the particle hit the ground?

A small heavy block is attached to the lower end of a light rod of length l which can be rotated about its clamped upper end. What minimum horizontal velocity should the block be given so that it moves in a complete vertical circle?
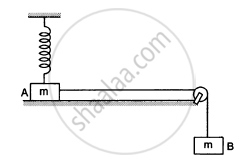
Figure following shows a light rod of length l rigidly attached to a small heavy block at one end and a hook at the other end. The system is released from rest with the rod in a horizontal position. There is a fixed smooth ring at a depth h below the initial position of the hook and the hook gets into the ring as it reaches there. What should be the minimum value of h so that the block moves in a complete circle about the ring?
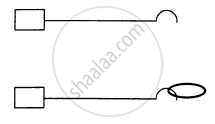
A spring of negligible mass and force constant 5 Nm–1 is compressed by a distance x = 5 cm. A block of mass 200 g is free to leave the end of the spring. If the system is released, what will be the speed of the block when it leaves the spring?
A particle is released from height S from the surface of the Earth. At a certain height, its kinetic energy is three times its potential energy. The height from the surface of the earth and the speed of the particle at that instant are respectively ______
Which of the diagrams shown in figure represents variation of total mechanical energy of a pendulum oscillating in air as function of time?
A baloon filled with helium rises against gravity increasing its potential energy. The speed of the baloon also increases as it rises. How do you reconcile this with the law of conservation of mechanical energy? You can neglect viscous drag of air and assume that density of air is constant.
A single conservative force acts on a body of mass 1 kg that moves along the x-axis. The potential energy U(x) is given by U (x) = 20 + (x - 2)2, where x is in meters. At x = 5.0 m the particle has a kinetic energy of 20 J, then the maximum kinetic energy of body is ______ J.
