Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Figure shows a particle sliding on a frictionless track which terminates in a straight horizontal section. If the particle starts slipping from point A, how far away from the track will the particle hit the ground?

Solution
Given,
Height of the starting point of the track, H = 1 m
Height of the ending point of the track, h = 0.5 m
Let v be the velocity of the particle at the end point on the track.
Applying the law of conservation of energy at the starting and ending point of the track,we get
After leaving the track, the body exhibits projectile motion for which,
So, the particle will hit the ground at a horizontal distance of 1 m from the other end of the track.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
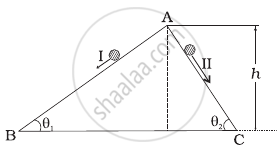
Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet at A from where two stones are allowed to slide down from rest, one on each track . Will the stones reach the bottom at the same time? Will they reach there with the same speed? Explain. Given θ1 = 30°, θ2 = 60°, and h = 10 m, what are the speeds and times taken by the two stones?

A particle is rotated in a vertical circle by connecting it to a string of length l and keeping the other end of the string fixed. The minimum speed of the particle when the string is horizontal for which the particle will complete the circle is
A heavy stone is thrown in from a cliff of height h in a given direction. The speed with which it hits the ground
(a) must depend on the speed of projection
(b) must be larger than the speed of projection
(c) must be independent of the speed of projection
(d) may be smaller than the speed of projection.
You lift a suitcase from the floor and keep it on a table. The work done by you on the suitcase does not depend on
(a) the path taken by the suitcase
(b) the time taken by you in doing so
(c) the weight of the suitcase
(d) your weight
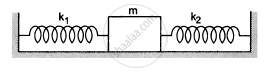
A block of mass m is attached to two unstretched springs of spring constants k1 and k2 as shown in the following figure. The block is displaced towards the right through a distance x and is released. Find the speed of the block as it passes through the mean position shown.
A small heavy block is attached to the lower end of a light rod of length l which can be rotated about its clamped upper end. What minimum horizontal velocity should the block be given so that it moves in a complete vertical circle?
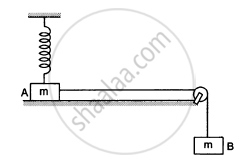
In the following figure shows two blocks A and B, each of mass of 320 g connected by a light string passing over a smooth light pulley. The horizontal surface on which the block Acan slide is smooth. Block A is attached to a spring of spring constant 40 N/m whose other end is fixed to a support 40 cm above the horizontal surface. Initially, the spring is vertical and unstretched when the system is released to move. Find the velocity of the block A at the instant it breaks off the surface below it. Take g = 10 m/s2.
One end of a spring of natural length h and spring constant k is fixed at the ground and the other is fitted with a smooth ring of mass m which is allowed to slide on a horizontal rod fixed at a height h (following figure). Initially, the spring makes an angle of 37° with the vertical when the system is released from rest. Find the speed of the ring when the spring becomes vertical.
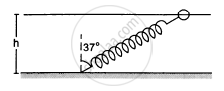
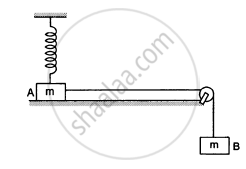
Figure following shows a light rod of length l rigidly attached to a small heavy block at one end and a hook at the other end. The system is released from rest with the rod in a horizontal position. There is a fixed smooth ring at a depth h below the initial position of the hook and the hook gets into the ring as it reaches there. What should be the minimum value of h so that the block moves in a complete circle about the ring?
A spring of negligible mass and force constant 5 Nm–1 is compressed by a distance x = 5 cm. A block of mass 200 g is free to leave the end of the spring. If the system is released, what will be the speed of the block when it leaves the spring?
A particle is released from height S from the surface of the Earth. At a certain height, its kinetic energy is three times its potential energy. The height from the surface of the earth and the speed of the particle at that instant are respectively ______.
A body is falling freely under the action of gravity alone in vacuum. Which of the following quantities remain constant during the fall?
Two inclined frictionless tracks, one gradual and the other steep meet at A from where two stones are allowed to slide down from rest, one on each track as shown in figure.
Which of the following statement is correct?
A mass of 5 kg is moving along a circular path of radius 1 m. If the mass moves with 300 revolutions per minute, its kinetic energy would be ______.
Why is electrical power required at all when the elevator is descending? Why should there be a limit on the number of passengers in this case?
A body falls towards earth in air. Will its total mechanical energy be conserved during the fall? Justify.
