Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A capacitor having a capacitance of 100 µF is charged to a potential difference of 50 V. (a) What is the magnitude of the charge on each plate? (b) The charging battery is disconnected and a dielectric of dielectric constant 2⋅5 is inserted. Calculate the new potential difference between the plates. (c) What charge would have produced this potential difference in absence of the dielectric slab. (d) Find the charge induced at a surface of the dielectric slab.
Solution
(a) The magnitude of the charge can be calculated as:
Charge = Capacitance × Potential difference
⇒ `Q = 100 xx 10^-6 xx 50 = 5 "mC"`
(b) When a dielectric is introduced, the potential difference decreases.
We know,
`V = "Initial potential"/"Dielectric Constant"`
⇒ `V = 50/2.5 = 20V`
(c) Now, the charge on the capacitance can be calculated as:
Charge = Capacitance × Potential difference
⇒ `q_f = 20 xx 100 xx 10^-6 = 2 "mC"`
(d) The charge induced on the dielectric can be calculated as :
`q = q_i(1-1/K) = 5 "mC" (1 - 1/2.5) = 3 "mC"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define 1 volt PD.
Draw a labelled diagram of Van de Graaff generator. State its working principle to show how by introducing a small charged sphere into a larger sphere, a large amount of charge can be transferred to the outer sphere. State the use of this machine and also point out its limitations.
The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change?
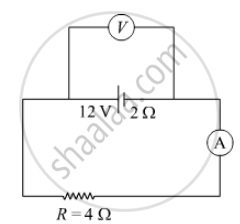
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
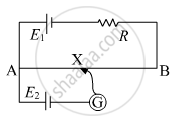
In the circuit diagram given below, AB is a uniform wire of resistance 15 Ω and length 1 m. It is connected to a cell E1 of emf 2V and negligible internal resistance and a resistance R. The balance point with another cell E2 of emf 75 mV is found at 30 cm from end A. Calculate the value of R.
Explain the principle of a device that can build up high voltages of the order of a few million volts.
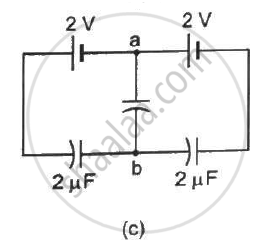
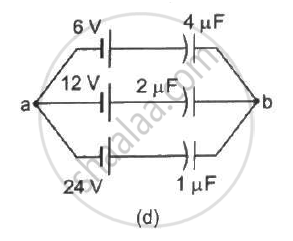
Find the potential difference `V_a - V_b` between the points a and b shown in each part of the figure.
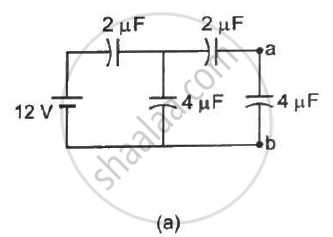
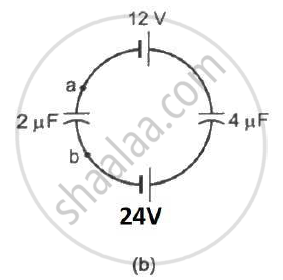
Find the potential difference between the points A and B and between the points B and C of the figure in steady state.

Answer the following question:
Find the expression for the resistivity of a material.
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
In circuits, a difference in potential from one point to another is often called ______.
If a positive charge moves in the direction of the electric field ______.
Assertion: Electric potential and electric potential energy are different quantities.
Reason: For a system of positive test charge and point charge electric potential energy = electric potential.
On moving a charge of Q coulomb by X cm, W J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is ______.
- It depends only on the initial and final position.
- It is the work done per unit positive charge in moving from one point to other.
- It is more for a positive charge of two units as compared to a positive charge of one unit.
A and B are two points in an electric field. If the work done in carrying 4.0C of electric charge from A to B is 16.0 J, the potential difference between A and B is:
An α-particle and a proton are accelerate at same potential difference from rest. What will be the ratio of their final velocity?
On moving a charge of 20 C by 2 cm, 2 j of work is done then the potential difference between the point is:-
A bullet of mass of 2 g is having a charge of 2 µc. Through what potential difference must it be accelerated, starting from rest, to acquire a speed of 10 m/s.
If potential difference between the two ends of a metallic wire is doubled, drift speed of free electrons in the wire ______.
