Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance ‘r’ is connected across a variable resistor ‘R’. Plot a graph showing the variation of terminal potential ‘V’ with resistance R. Predict from the graph the condition under which ‘V’ becomes equal to ‘E’.
Solution
V becomes equal to E when no current flows through the circuit.
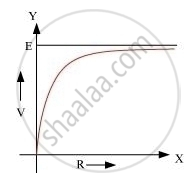
The condition under which V will be equal to E is when R = ∞
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
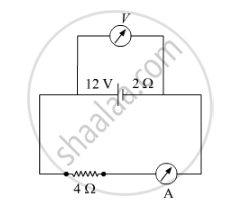
A battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to a 4 Ω resistor as shown in the figure.
(a) Show that a voltmeter when placed across the cell and across the resistor, in turn, gives the same reading.
(b) To record the voltage and the current in the circuit, why is voltmeter placed in parallel and ammeter in series in the circuit?
A cell of emf 'E' and internal resistance 'r' is connected across a variable resistor 'R'. Plot a graph showing variation of terminal voltage 'V' of the cell versus the current 'I'. Using the plot, show how the emf of the cell and its internal resistance can be determined.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.25 V gives a balance point at 35.0 cm length of the wire. If the cell is replaced by another cell and the balance point shifts to 63.0 cm, what is the emf of the second cell?
Six lead-acid types of secondary cells each of emf 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.015 Ω are joined in series to provide a supply to a resistance of 8.5 Ω. What are the current drawn from the supply and its terminal voltage?
A resistor R is connected to a cell of-emf e and internal resistance r. The potential difference across the resistor R is found to be V. State the relation between e, V, Rand r.
Can the potential difference across a battery be greater than its emf?
Consider N = n1n2 identical cells, each of emf ε and internal resistance r. Suppose n1 cells are joined in series to form a line and n2 such lines are connected in parallel.
The combination drives a current in an external resistance R. (a) Find the current in the external resistance. (b) Assuming that n1 and n2 can be continuously varied, find the relation between n1, n2, R and r for which the current in R is maximum.
A battery of emf 100 V and a resistor of resistance 10 kΩ are joined in series. This system is used as a source to supply current to an external resistance R. If R is not greater than 100 Ω, the current through it is constant up to two significant digits.
Find its value. This is the basic principle of a constant-current source.
A cell of emf E and internal resistance r is connected across an external resistance R. Plot a graph showing the variation of P.D. across R, versus R.
Three cells, each of emf E but internal resistances 2r, 3r and 6r are connected in parallel across a resistor R.
Obtain expressions for (i) current flowing in the circuit, and (ii) the terminal potential differences across the equivalent cell.
