Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A circular hole of diameter 2.00 cm is made in an aluminium plate at 0°C. What will be the diameter at 100°C? α for aluminium = 2.3 × 10–5 °C–1.
Solution
Given:
Diameter of a circular hole in an aluminium plate at 0°C, d1 = 2 cm = 2 × 10–2 m
Initial temperature, t1 = 0 °C
Final temperature, t2 = 100 °C
So, the change in temperature, (Δt) = 100°C - 0°C = 100°C
The linear expansion coefficient of aluminium, αal = 2.3 × 10–5 °C–1
Let the diameter of the circular hole in the plate at 100oC be d2 , which can be written as
d2 = d1(1+αΔt)
⇒ d2 =2 × 10-2(1+2.3×10-5×102)
⇒ d2 = 2×10-2(1+2.3×10-3)
⇒ d2 = 2×10-2+2.3×2×10-5
⇒ d2 = 0.02 +0.000046
⇒ d2 =0.020046 m
⇒ d2 ≈ 2.0046 cm
Therefore, the diameter of the circular hole in the aluminium plate at 100oC is 2.0046 cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define emissive power and coefficient of emmision of a body.
Answer the following:
There were two fixed points in the original Celsius scale as mentioned above which were assigned the number 0 °C and 100 °C respectively. On the absolute scale, one of the fixed points is the triple-point of water, which on the Kelvin absolute scale is assigned the number 273.16 K. What is the other fixed point on this (Kelvin) scale?
A body cools from 62°C to 54°C in 10 minutes and to 48°C in the next 10 minutes. Find the temperature of the surroundings.
The density of water at 4°C is supposed to be 1000 kg m–3. Is it same at sea level and at high altitude?
Which of the curves in the following figure represents the relation between Celsius and Fahrenheit temperatures?
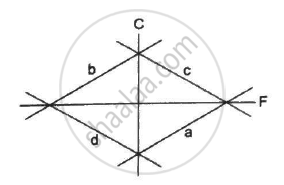
If the temperature of a uniform rod is slightly increased by ∆t, its moment of inertia I about a line parallel to itself will increase by
An aluminium sphere is dipped into water at 10°C. If the temperature is increased, the force of buoyancy
As the temperature is increased, the time period of a pendulum
When a hot liquid is mixed with a cold liquid, the temperature of the mixture ____________ .
The temperature of a solid object is observed to be constant during a period. In this period
(a) heat may have been supplied to the body
(b) heat may have been extracted from the body
(c) no heat is supplied to the body
(d) no heat is extracted from the body
A steel ball that is initially at a pressure of 1.0 × 105 Pa is heated from 20°C to 120°C, keeping its volume constant.
Find the pressure inside the ball. Coefficient of linear expansion of steel = 12 × 10–6 °C–1and bulk modulus of steel = 1.6 × 1011 Nm–2.
Define one mole.
Two tumblers of A and B have water at 50°C temperature. If the water from A and B is poured into tumbler C. The temperature of C is ______.
Heat is measured in Celsius or centigrade.
The degree of hotness and coldness of a body is called ______.
An earthen pitcher loses 1 gm of water per minute due to evaporation. If the water equivalent of the pitcher is 0.5 kg and the pitcher contains 9.5 kg of water, calculate the time required for the water in a pitcher to cool to 28°C from the original temperature of 30°C. Neglect radiation effects. The latent heat of vaporization in this range of temperature is 580 Cal/gm and the specific heat of water is 1 Cal/gm°C.
Heat given to a body that raises its temperature by 1°C is ______.
